Indicators
The contracts entered into by Banrisul, and its associate companies focus on the appropriate treatment of their technical staff, who has a direct role in the provision of services. The contractor is responsible for ensuring this appropriate treatment, while the Bank assumes joint responsibility for supervising these practices, complying with state laws and the Federal Constitution. All contracts have provisions on social criteria, and all contracts entered into by Banrisul have specific clauses related to labor and social issues, in compliance with the specific legislation.
After the Management Proposal is published, the shareholders make nominations for the Board of Directors, which are subsequently submitted to the Chief of Staff of the Government of the State of Rio Grande do Sul for approval. If the nominations are approved, their names and information will be forwarded to the Treasury Department for the opening of an administrative proceeding via the PROA system. Upon the receipt of the Administrative Proceeding, the Eligibility and Compensation Committee analyzes the nominee, taking into consideration the eligibility requirements outlined in the Nomination and Succession Policy, which determine that the background and experience of the nominees for the Board of the Directors should be assessed, as well as their time availability to perform the duties, diversity, knowledge, experience, behavior, cultural aspects, age group, and gender. The Committee’s opinion is forwarded to the State Attorney General’s Office for a final decision about the fulfillment of the requirements and the absence of impediments. Once the nomination has been approved by the State Attorney General’s Office, the proceeding returns to the Company, so that the election can be held.
Every two years, before the Annual and Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting, shareholders submit their candidates for the highest governance body. The controlling shareholder makes its nominations considering the criteria set forth in the current legislation (Federal Law 13,303/16; Federal Law 6,404/46 and State Decree RS 54,110/18).
In 2022, the Nomination and Succession Policy was updated and stated that the election of Banrisul’s Board of Directors members, should include seats for Diversity groups as of 2023, as follows: I – the shareholder, or group of shareholders, with a right to nominate 25-40% of seats on Banrisul’s Board of Directors, shall be responsible for allocating at least one of the openings for members of the Diversity group; II – the shareholder, or group of shareholders, with a right to nominate for Banrisul’s Board of Directors any percentage higher than that established in item I must allocate two or more openings for members of the Diversity group; III – Grupo Banrisul must adjust the composition of the Boards of Directors, which shall respect the minimum percentage of 30% for openings aimed at the Diversity group, by 2030.
Independence criteria must also be considered, as provided for in article 22 of the Bylaws, which can be read here.
Banrisul’s current eligibility process involves several spheres (State Department of Finance, State Chief of Staff and State Attorney General’s Office, among others). This verification flow conveys security and reliability to all stakeholders.
For the unbanked public involved in financial education strategies, the engagement numbers were as follows:
| Public | Participations | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | |
| Projeto Pescar | 40 | 40 |
| Jovem Aprendiz | 20 | 70 |
| Students | - | 116 |
| Nova Geração Caldeira | - | 50 |
No potential risks of child labor or young workers exposed to hazardous work were identified in the Institution’s operations.
Suppliers, especially those with contracts involving the outsourcing of labor, are submitted to thorough checks for compliance with labor and social security obligations, monitoring certificates of good standing, among other actions.
Regarding customers, Banrisul conducts checks to make sure they have all applicable certificates and licenses, in addition to assessing their history of non-compliance.
No potential risks for incidents of forced labor were identified in the Institution’s operations.
As for suppliers, Banrisul closely supervises compliance with labor and social security obligations through the monitoring of certificates of good standing, among other actions.
Customers are checked against a list of employers of who use compulsory labor published by the Ministry of Labor and Employment.
According to Banrisul’s Anti-Corruption Policy, all those subject to the Policy are responsible for fostering an ethical culture and for creating an environment of permanent corruption control and prevention, in which it is possible to monitor and identify, through Due Diligence procedures, operations from customers and non-customers – individuals and companies – and actions or suspected corruption crimes, as well as enforcing the internal integrity and auditing mechanisms and procedures, encouraging whistleblowing and the effective application of Banrisul’s Anti-Corruption Policy and Code of Ethics and Conduct.
Moreover, in 2021, a Social, Environmental and Climate Risks (RSAC, in Portuguese) assessment questionnaire was developed for operations over R$10 million, which includes anti-corruption questions.
Operational risk management includes identifying and assessing external fraud events, the possibility of employee misconduct that offers or results in undue advantage and operational flaws in developing processes to assess or identify suspicious operations.
The Bank is subject to Brazilian and foreign anti-corruption legislation. These laws require the adoption of integrity procedures in order to mitigate the risk that any person, acting on behalf of the Bank, may offer an undue advantage to a public agent, in order to obtain benefits of any kind. The transnational scope legislations, including, but not limited to, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977 and the UK Bribery Act of 2000, in addition to Federal Law no. 12,846/13, provide for the adoption of specific policies and procedures for the prevention and fight against illegal acts related to corruption of public administration entities and government representatives, which aim at ensuring any kind of advantage. They also require the Bank to keep its books and records accurate and rely on an internal controls system to certify their respective veracity, in addition to the prevention of illegal activities.
There is no percentage of assets subject to positive or negative social or environmental screening.The Agribusiness Department does not use screening criteria. However, before contracting a transaction, the department runs a social and environmental compliance check to verify social issues (forced labor, IBAMA and ICMBio embargoes, administrative improbity and ineligibility) and environmental issues (overlap of the area to be financed with land reform settlement areas, indigenous land, quilombola territory, conservation units, areas embargoed by IBAMA or ICMBio, areas susceptible to flooding, archaeological sites and areas with deforestation alerts. Moreover, in order to grant rural credit, the Bank requires environmental licensing of the financed activity.
| Performance Assessment per Category³ | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | Men | Women | |
| Managers¹ | 23.7% | 38.7% | 21.6% | 36.0% | 25.6% | 41.3% |
| Supervisors | 62.2% | 76.4% | 60.6% | 72.2% | 59.2% | 71.3% |
| Total² | 31.4% | 48.5% | 28.9% | 44.1% | 31.2% | 47.3% |
¹ It includes the following employee categories: account manager, market manager, agribusiness relationship manager and business manager (corporate, other states and government).
² It considers all of the Company’s employees.
³ Only those categories that receive performance and competence assessments as a result of the in-house training courses specified in note 1 were taken into account.
The Institution is grounded on its values defined in its Code of Ethics as transparency, ethics, commitment, integration and efficiency, as well as in principles and guidelines, such as integrity, respect for diversity, people, appreciation of work, social and environmental responsibility, respect for competition, respect for the image and excellence in rendering services.
The commitments refer to internationally recognized intra-governmental instruments, namely the Brazilian Central Bank, Febraban, National Monetary Council, UN Global Compact Guidelines and SDG 16.
These guidelines/policies set forth responsibilities and consequences for all levels.
Banrisul manages capital and credit, market, interest rate variation risks for the instruments classified in the banking portfolio – IRRBB- in a continuous and integrated manner; as well as liquidity, operational, social, environmental, climate and other risks considered relevant.
Social risk, defined as the possibility of the Institution incurring in losses from events related to the violation of fundamental rights and guarantees or by acts that are harmful to the common interest, is one of the relevant risks included in the Risk Management Policies.
Banrisul does not have a specific human rights policy.
Human rights are rules that recognize and protect the dignity of all human beings and govern how individual human beings live in society and among themselves, as well as their relationship with the State and the obligations that the State has in relation to them. In this regard, as a signatory to the Global Compact since 2013, Banrisul reaffirms its commitment to the well-being of its employees, as well as to seeking to ensure the rights of its customers, suppliers and all stakeholders to which it engages. The Bank manages social risk, particularly, in order to mitigate possible actions that may occur under the human rights aspect.
The stakeholder categories to whom the Organization pays special attention in this commitment are employees, customers, suppliers and vulnerable publics.
Policy commitments should be approved by the Board of Directors. These commitments apply to management members, board members, employees, interns, members of the Banrisul Group, business partners, suppliers and the Group’s service providers.
An Administrative Instruction is issued stating that all employees must sign a Compliance Agreement, which is published in the Institutional Manual (Chapter 04 of Banrisul’s Code of Ethics and Conduct).
All employees receive training on the Code of Ethics and Conduct and the Anti-Corruption Policy. Banrisul has other institutional policies and makes a whistleblowing channel available both on the internal and external websites. The commitments of the Code of Ethics and the Anti-Corruption Policy are available to the public.
In 2022, Banrisul conducted a complete materiality assessment to define its material topics, which encompassed peer benchmarking, as well as analysis of the Company’s internal documents and industry literature, such as ESG ratings and standards. A list of material topics for the industry was prepared based thereon. This list was discussed and validated with important stakeholders through interviews (the CEO, Sustainability Corporate Department and Executive Board) and, then it was prioritized through an online survey with a larger stakeholder group.
At the same time, based on the analysis of internal risk documents, the Company assessed possible impacts related to each topic, which were duly classified as regards their nature and then added to the consolidated materiality results.
Results were assessed using a methodology that weighted the answers according to each stakeholder group. The results of the online survey were consolidated to the topics’ impact study to prepare the final list of material topics.
A total of 1,315 people from the following stakeholder groups participated in the online survey:
- Employees;
- Shareholders/investors (priority);
- Shareholders/investors (diversified);
- Capital markets;
- Customers;
- Main suppliers;
- Government;
- Representatives of non-profit organizations and/or social institutions;
- Specialized media outlets;
- Union representatives;
- Executive Officers;
- Board of Directors members;
- Sustainability Committee members.
Prioritization and final approval:
Sustainability Corporate Department, CEO and Administrative Executive Board. The materiality results were also presented to the Sustainability Committee, the Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Committee and the Executive Board.
The responsibilities of the Eligibility and Compensation Committee are:
(i) drafting the compensation policy for Management of the Bank and its subsidiaries, suggesting to the respective Boards of Directors various forms of fixed and variable compensation, in addition to benefits and special recruiting and severance programs;
(ii) proposing to the Boards of Directors of the Bank and subsidiaries the overall Management compensation amount to be submitted to the respective Shareholders’ Meetings, pursuant to Article 152, of Law 6,404, of 1976;
(iii) assessing future internal and external scenarios and their possible impacts on the Management compensation policy of the Bank and its subsidiaries;
(iv) analyzing the Management compensation policy of the Bank and its subsidiaries vis-à-vis market practices in order to identify significant discrepancies compared its peers, proposing the necessary adjustments.
As per CMN Resolution 3,921/10, the Eligibility and Compensation Committee is responsible for assisting in the process of determining compensation. The Committee is composed of three independent members, all of whom are natural persons residing in Brazil, with higher education degrees and technical skills suitable for the position they hold. The members also meet the criteria for holding positions in statutory bodies of financial and other institutions authorized to operate by the Brazilian Central Bank.
The board members convene in ordinary and extraordinary meetings, and their considerations are recorded in minutes. In turn, shareholders can express their opinions at the Annual/Extraordinary Shareholders Meeting.
The Board of Directors members are only entitled to fixed monthly compensation as fees, and are not entitled to variable compensation or direct and/or indirect benefits. Executive Board members are entitled to monthly compensation in the form of monthly wage plus a representation fee, the annual amount of which must not exceed the overall management compensation amount set by the Extraordinary and Annual Shareholders’ Meeting. They are also entitled to Banrisul’s Profit Sharing Program (PLR, in Portuguese), calculated in accordance with the rules established by the Board of Directors, considering the rules applicable to the payment of PLR to employees, as defined in the Banking Employees’ Collective Bargaining Agreement. In addition to the PLR, the Banrisul Conglomerate may pay variable compensation to its executive officers, provided it is included in the overall compensation approved by the Shareholders’ Meeting, observing the limits established by the legislation in force and based on criteria that may be defined by the Board of Directors.
The report is published every year and this reporting period is between January 1, 2022 and December 31, 2022.
Contact: Sustainability Corporate Department, Rua Caldas Júnior, 108, 6º andar
E-mail: Sustentabilidade@banrisul.com.br
No information has been restated in previous reporting periods.
The composition of the Board of Directors ensures a seat for common minority shareholders, preferred minority shareholders and a representative of the employees, who is chosen by internal election, according to the Board of Directors Charter. Thus, stakeholder groups are engaged in the Board of Directors meetings.
The Board of Directors is responsible for the Company’s overall direction of business, institutional guidelines and goals. As regards Integrated Capital and Corporate Risk Management, the Board is responsible for:
a) Establishing the Institution’s risk appetite levels in the Risk Appetite Statement (RAS) and reviewing them supported by the Risk Committee, the Executive Board and the Chief Risk Officer (CRO);
b) Ensuring compliance with the Institution’s policies, strategies and risk management limits;
c) Whenever necessary, authorizing exceptions to policies, procedures, limits and risk appetite levels set out in the RAS;
d) Ensuring that the Institution’s compensation structure does not encourage behaviors that are incompatible with risk appetite levels set out in the RAS;
e) Ensuring that the Institution keeps adequate and sufficient capital and liquidity levels;
f) Having a broad and integrated knowledge of risks that can hinder capital.
As for Corporate Risk Management, the Board of Directors, the Risk Committee, the CRO and the Executive Board have seral joint responsibilities, including:
a) Understanding, in a broad and integrated way, risks that can impact the Institution’s capital and liquidity;
b) Understanding the limits of information included in capital and risk management reports;
c) Ensuring that the Institution complies with the content of the RAS;
d) Understanding the limits and uncertainties related to the assessment of risk models, even when they are developed by a third party, and the methodologies used in risk management structure; and
e) Ensuring the Institution’s different levels understand and continually monitor risks.
The Board of Directors meets periodically to evaluate changes to the capital and corporate risk management policies, as well as management reports on the main risks to which the Institution is exposed. At Management level, Banrisul relies on the Corporate Risk Committee and the Control and Risk Executive Office and, statutorily, on the Statutory Risk Committee.
In compliance with CMN Resolution 4,945, of September 15, 2021, Banrisul’s Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Policy (PRSAC, in Portuguese) determines that it is incumbent upon the Executive Board, a governance body elected by the Board of Directors, to:
a) provide input and participate in the decision-making related to the drafting and review of the PRSAC, assisting the Board of Directors;
b) support the implementation of actions to ensure this Policy’s effectiveness;
c) monitor and evaluate implemented actions;
d) ensure that implemented actions are improved whenever possible deficiencies are identified;
e) help and encourage the adequate and reliable dissemination of mandatory information;
f) manage the PRSAC at Banrisul. The responsibilities of the Board of Directors include ensuring that the Institution complies with the PRSAC and taking measures to ensure its effectiveness.
Banrisul has a the Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Committee (CRSAC, in Portuguese), an advisory body to the Board of Directors, whose duties and responsibilities are to:
a) make recommendations to the Board of Directors on the drafting and review of the Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Policy;
b) evaluate if the actions implemented are in compliance with the Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Policy and, whenever necessary, make recommendations for improvement;
c) keep records of its deliberations and decisions;
d) evaluate and monitor the Bank’s sustainable performance and the effectiveness of the actions laid down in the Sustainability Plan;
e) monitor advancements in sustainability, seeking to identify opportunities and risks, in order to create value for the Bank and its stakeholders;
f) propose and follow-up the execution of initiatives that improve the Bank’s socio-environmental performance;
g) assisting the Board of Directors in incorporating sustainability into the Company’s business strategy and administrative practices and follow up its progress;
h) analyze, monitor and issue recommendations and opinions to support the Board of Directors’ decisions on policies and practices related to its field;
i) fulfil other duties determined by the Board of Directors.
The Message from the CEO can be found in the Sustainability Report on page 4.
The Ombudsman’s Office classifies the complaints received by its channels into topic, item and root cause. Regarding subject, there is a “bank secrecy” item, which is under the topic “other subjects” and the root cause “LGPD” (Brazilian General Data Protection Law). In 2022, five customer complaints were filed related to bank secrecy and/or LGPD, including in external agencies; four of these complaints were classified as invalid and only one was classified as valid (not resolved). In the latter, there was proof of a data breach.
The report classified was valid was received through the Consumer Protection Agency (Procon, in Portuguese)/RS (external agency).
| Waste generated by type and destination (t) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
| Hazardous waste (Class I) - diverted from disposal | |||
| Batteries- Recycling | 0 | 0 | 0,1 |
| Non-hazardous waste (Class II) - diverted from disposal | |||
| Banners, shredded cardboard and acrylic - Recycling | 0 | 2,8 | 0 |
| Structured network cables - Reverse logistics | 0 | 0 | 0,1 |
| Vaults - Recycling¹ | 0 | 10,4 | - |
| Electronic devices - Recycling | 49,7 | 93,4 | 31,4 |
| Paper and cardboard - Recycling | 128,5 | 206,6 | 233,5 |
| Metal scraps -Recycling | 45,4 | 114,1 | 76,4 |
| A) Total waste diverted from final disposal | 224 | 427,3 | 341,6 |
| Non-hazardous waste (Class II) - directed tod disposal | |||
| Co-processing | 0,3 | 1,5 | 0 |
| Waste directed to landfills² | 0 | 0 | 125,0 |
| B) Total waste directed to final disposal | 0,3 | 1,5 | 125,0 |
| Total generated waste in tons (A+B) | 223,9 | 428,8 | 466,6 |
1In 2022, we did not have vaults sent for recycling, with only the donation of these items for reuse. In this case, as it is a donation, they are considered in units in the item dealing with the donation of furniture.
2The organic solid waste generated in the organization is destined for public collection in the localities where the agencies are present. In the administrative headquarters building there is a company contracted to dispose of organic waste. Until 2021 there was no measurement of the amount of this waste generated.
| Waste generated by type and destination (units) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
| Hazardous waste (Class I) - directed to disposal | |||
| Lamps - Recycling | 1.652 | 2.060 | 2.734 |
| Tonners - Reverse logistics³ | - | - | 621 |
| A) Total waste diverted from final disposal | 1.652 | 2.060 | 3.355 |
| Non-hazardous waste (Class II) - diverted from disposal | |||
| Furniture donation - Reuse⁴ | 2.127 | 4.999 | 2.391 |
| B) Total waste diverted from final disposal | 2.127 | 4.999 | 2.391 |
| Total generated waste in units (A+B) | 3.779 | 7.059 | 5.746 |
3From 2022, we started to inform the data regarding tonners forwarded to reverse logistics
4The safes donated for reuse are added to this item.
The number of workers who are not employees and whose work is controlled by the organization amounts to 2,204, of whom four are supernumeraries and 2,200¹ are interns.
Most common workers are interns, whose contractual relationship is established through an integration agent called Center for Company and School Integration (CIEE, in Portuguese). Interns serve bank customers, act as cashiers, provide documents to customers and perform collection activities. They also provide supporting services to the branches and other Bank departments, manage the flow of bank bags, clear documents and control documents in the archives.
The methodology and assumptions used to obtain this indicator gather data from the internal database. The significant change in the number of workers is due to the duration of the internship contract, which is up to two years.
¹ The 2022 Administration Report shows 2,293 trainees. The difference is due to the criteria used in the consultation, which also included those who left during the month. After adjustments, those who left during the month were disregarded for the purposes of the Sustainability Report.
The ratio of the annual total compensation for the organization’s highest-paid individual to the median annual total compensation for all employees is 12.0%, while the ratio of the percentage increase in the annual total compensation for the organization’s highest-paid individual to the median percentage increase in the annual total compensation for all employees is 0.8%.
Annual salary increases occur in April (regulatory promotions retroactive to January) and in September (collective bargaining agreement).
For calculation purposes, the CEO, who is not a Bank employee, was considered as the highest-paid individual. The other workers who are not employees were not considered in the calculation. The total compensation (salaries, bonuses, job commission, full performance bonus, annual bonus, overtime, singing bonus, relocation bonus, management, retirement bonus, and retirement incentive) was considered in calculating compensation.
Banrisul operates in the public and private sectors. The Bank and its affiliates currently have several types of suppliers: lawyers; consultants; system analysts; sellers of perishable and non-perishable goods; international IT companies; armored truck companies; and numerous other service providers.
The number of direct suppliers, in 2022, is estimated at 1,093. The Bank hires suppliers to provide services and products unrelated to its core activity, i.e., they provide supporting services and products, including security, cleaning, transportation of valuables, acquisition of IT systems, telephone and internet services, acquisition of furniture, building rental, acquisition of sundry items.
Banrisul acts as a financial agent for customers, from industry, agriculture, transport, service, trade and health sectors. Most of them are located in Brazil’s South region.
Stakeholder categories with whom Banrisul engages are:
- Employees;
- Shareholders/investors;
- Market analysts;
- Customers;
- Suppliers;
- Government;
- Unions;
- Executive Board;
- Board of Directors;
- Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Committee – CRSAC.
The Institution has identified the need to create a stakeholder engagement program to strengthen its relationship with these groups and provide greater business opportunities and chances to listen to them. The goal is that this program enables the Institution to explore relationship channels with several groups.
For preparing its materiality, Banrisul surveyed all its target audiences, creating an opportunity to get to know their interests.
| Average training hours per employee, by gender | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Δ 2021/2022 |
| Men | 37.1 | 45.7 | 67.0 | 46.5% |
| Women | 32.4 | 42.7 | 65.3 | 52.9% |
| Total training hours | 34.5 | 47.3 | 66.1 | 39.9% |
| Average training hours per employee, by employee category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employee category | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Δ 2021/2022 |
| Superintendent | 14.3 | 20.3 | 44.4 | 118.5% |
| Manager | 59.6 | 57.5 | 114.7 | 99.5% |
| Analyst | 11.9 | 29.7 | 39.6 | 33.3% |
| Assistant | 11.4 | 19.6 | 31.3 | 59.7% |
| Without commissioned position | 33.6 | 38.8 | 64.3 | 65.7% |
| Interns | 16.8 | 36.4 | 55.8 | 53.4% |
| Other | 78.7 | 31.1 | 66.0 | 112.1% |
Card-related losses incurred in the reporting period totaled R$1.8 million.
The Chair of the Board of Directors is not the Company’s CEO.
100% of employees are covered by collective bargaining agreements.
In compliance with Law 13,303/16, every year, elected Management members attend specific training on corporate and capital market legislation, disclosure of information, internal controls, code of conduct, Law 12,846, of August 1, 2013 (Anti-Corruption Law) and other topics related to the activities of a publicly held company or government-controlled company. In 2022, ESG was included in the list of topics. Additionally, Management members may participate in other courses/events with themes pertinent to their responsibilities in the respective governance bodies, if said theme is interesting for the Company.
The Business Partnership and Open Banking Department has been working constantly with Bem Promotora on the Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing (PLDFT, in Portuguese). In September 2022, Banrisul published its New Policy on Prevention of Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and the Distribution of Weapons of Mass Destruction, which is a mandatory reading for all those operating the corresponding assets. This document was read by 1,440 operators.
Suspicions or evidence of non-compliance with Banrisul’s Code of Ethics and Conduct, policies, standards and institutional regulations in force should be reported through the Whistleblowing Channel, which allows the anonymous reporting of the misconduct, ensuring the right to confidentiality and protection against retaliation. The internal and external channels are available, respectively, on the Corporate Intranet and on Banrisul’s website (www.banrisul.com.br) and are intended for receiving misconduct reposts and complaints from employees and other stakeholders. The Control and Compliance Department is the independent area responsible for managing this channel.
Every six months the Board of Directors reviews a report on Banrisul’s Whistleblowing Channel. In compliance with article 3, paragraph 2, of CMN Resolution 4,859/2020, the Control and Compliance Department prepares a report with the following minimum information:
I – the number of reports received;
II – the nature of the reports;
III – the departments responsible for handling the situation;
IV – the average response time; and
V – the measures adopted by the Institution.
In 2022, there were 1,085 significant instances of non-compliance with laws and regulations, of which only one incurred in fine (one instance of irregular waste disposal). 720 Municipal Tax Unit (UFM, in Portuguese) (R$3,554.06) repaid by the outsourced cleaning company (as set forth in the contract) and other non-monetary penalties. Out of the 1,084 administrative or judicial proceedings that did not incur in fines, 1,082 are social in scope: six are events related to accessibility, 20 to over-indebtedness, one to customer moral harassment, 1,055 are labor complaint events (according to CMN Resolution 4,943/21), one environmental event (disposal of recyclable waste in an organic waste container), one climate-related event (collection lawsuit to recover the amounts from the plaintiff’s property insurance policy, affected by a storm).
Additionally, Banrisul received 262 notifications in this reporting cycle, 45 of which were fines for instances of non-compliance with laws, and all of these were paid during previous reporting periods.
Strictly speaking, the Bank did not identify incidents of corruption in the form of offering or requesting of undue advantages. Banrisul did not terminate or refuse to renew contracts due to the involvement or possible involvement of a correspondent in corruption. Neither the Organization nor its employees are parties to corruption-related lawsuits.
Banrisul’s Board of Directors identifies and manages conflicts of interest based on, but not limited to, applicable legal standards provided for in Article 156 of the Brazilian Corporate Law and article 25 of its Bylaws. Furthermore, the Code of Ethics and Conduct is widely disseminated to management members, board members, employees, interns, members of the Banrisul Group, business partners, suppliers and service providers. In the event of a potential conflict of interest, members of the Board of Directors, the Audit Committee and the Ethics Committee must abstain from resolving on matters in which this conflict is identified. Another important document governing this topic is the Related-Party Transactions Policy that outlines the conditions credit transactions and other related-party transactions.
The item “SUBORDINATION, SERVICE OR CONTROL RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN THE ISSUER’S MANAGEMENT AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES, AFFLIATES AND OTHERS” of the Company’s Reference Form informs the interest held by Banrisul management in management of other companies in the Banrisul Group. The only controlling shareholder is the State of Rio Grande do Sul.
Related-party transactions, as well as measures taken by Banrisul, can be found in Note 29, pages 118 and 119, to the 2022 Financial Statements, available here.
The Control and Risk Executive Office is responsible for managing the Institutions’ corporate risks.
As regards Integrated Capital and Corporate Risk Management, the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) is responsible for the Corporate Risk Management Department and his/her duties include ensuring that the risk process monitors, controls, evaluates and plans capital need and goals and identifies, measures, monitors, reports, controls and mitigates credit, market, IRRBB, liquidity, operational, social, environmental and climate risks associated with the Prudential Conglomerate, communicating said risks to the Risk Committee, the CEO, the Board of Directors and regulatory agencies.
The Corporate Risk Executive Superintendent reports to the CRO on the Institution’s risk management. At least every year, risk management reports are submitted to the Board of Directors for consideration.
At Banrisul, the analysis of credit risk is carried out through statistical models for individuals and for the mass corporate segment, which comprises companies with average monthly income of up to R$2 million that do not belong to economic groups and/or exceptional segments.
The exceptional segment is identified based on the company’s main activity in the national classification of economic activities (CNAE, in Portuguese) and includes companies that have atypical cash flows, as well as those that are not targets of Banrisul’s market of interest.
In the segments with little commercial interest, we list the segments with high environmental and social risk. Companies that are not subject to the mass analysis are analyzed on a case-by-case basis observing quantitative and qualitative aspects.
The Bank currently checks with external agencies whether the customer, either an individual or a company, has been listed as an “Employer that uses Forced Labor” or as causing “Environmental Damage” (conviction for environmental damage in actions filed by Brazil’s environmental protection agency (IBAMA, in Portuguese)). Potential new customers identified as an “Employer that uses Forced Labor” are not allowed to obtain credit of any type. If existing customers are included in this list, Banrisul takes specific measures to discontinue the business relationship. The occurrence of environmental damage, on the other hand, prevents customers from obtaining specialized credit lines.
Regarding social aspects, there are markings in the Risk Calculation and Negative Occurrence systems indicating individual customers classified based on a proprietary model to identify vulnerabilities, in which customers with a high score go through a special credit granting process, with the application of regulations to product policies. In addition, the credit granting guidelines define the overall limits that should be considered in the process, preventing over-indebtedness.
Moreover, in larger transactions, especially those involving larger companies or exceptional segments (for which we do not set limits using a mass model), Banrisul carries out a case-by-case analysis using data from the financial statements, notes to the financial statements and other information, in addition to requiring the filling out of a specific checklist to learn more about the customer, helping analysts obtain qualitative information that will be used in their report and risk analysis, as well as in the definition of the exposure limit.
In order to include a qualitative aspect in credit analysis, Banrisul incorporated an ESG assessment tool into the process. The tool uses a questionnaire completed by companies/economic groups with exposure or proposed risk limit higher than R$5 million to generate a score that is incorporated into the customer’s internal risk rating. It is being used to assess the risk limit of sectors considered to be more sensitive to ESG aspects. ESG aspects are analyzed qualitatively by credit risk analysts in line with Banrisul’s Institutional Manual/Social, Environmental and Climate Policy.
The risk analysis for the establishment of the exposure limit is general in nature, i.e., it addresses the most relevant information and considerations for credit risk without taking account the specific characteristics of the credit lines in question. In this context, additional information and analyses can be required during the credit analysis and approval process, with special attention to ESG aspects, especially credit lines for investment, agribusiness and real estate projects.
Given the relevance of credit exposures, all the transactions above R$10 million in which the allocation of funds or credit granted is known are subject to the completion of standardized questionnaires to better measure the social, environmental and climate risk. This questionnaire may also be used in other transactions or in transactions involving a lower amount.
The guidelines related to the products, which complement the Institution’s Credit Policy, are set out in the specific regulations for Agribusiness (N7), Development (N33) and Real Estate (N30).
In order to estimate credit losses during the duration of the contract of the financial assets, the provision for credit losses is calculated monthly for all active contracts based on the rating calculation. Currently, the credit rating of Banrisul’s credit transactions can be hurt if the client does not have an approved credit exposure limit. For some industries, this individual analysis to determine exposure limit is forbidden, for example sectors/CNAE of gambling and betting, several agricultural crops (such as tobacco and sugar cane).
In the context of the Stress Test Program, the scenario is assessed in two stages. At first, the accounting balance of the adverse scenario is used in the ad hoc scenario analysis. All transactions classified as highly exposed to climate risk are downgraded by one level of risk, resulting in a higher provision. The difference between the new provision and the initial provision is then added to the amount of the expected difference between the loss in the adverse scenario and the loss in the credit base scenario.
These data are sent to the budget department, which will calculate the income statement with these new provision amounts, attesting to the Institution’s resilience in the face of a possible stress. Whereas the individualized analyses make use of, but are not limited to, relevant information from the ESG agenda, the knowledge acquired during these analyses, combined with the constant monitoring of trends, is how we currently seek to identify opportunities for improvements in our processes.
As we monitor the credit portfolio, we look at credit allocation according to the sector, as well as the largest individual and economic group exposures. In the geographical context, the statistical models used in credit granting include a variable that indicates the main regions of the state.
The Green Taxonomy (Brazilian Federation of Banks — FEBRABAN, in Portuguese) is used to analyze the risk exposure profile. The assessment is based on the borrower’s code in the National Classification of Economic Activity (CNAE) in three dimensions: Contribution to the Green Economy, Exposure to Climate Change and Exposure to Environmental Risk.
The activities listed in Resolution 237/97 of the National Environmental Council (CONAMA, in Portuguese), which requires environmental licensing for sectors with higher potential impact, were considered in the classification of the Exposure to Environmental Risk. In December 2022, 41.49% of the corporate credit portfolio had high exposure to environmental risk.
The classification related to Exposure to Climate Change was prepared based on the activities defined by Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) as having the highest probability of being affected by transition and physical risks considering three factors: greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, energy use and water consumption. These sectors were classified as High Exposure, and the activities related to or financially exposed to this sector were classified as Moderate Exposure. In December 2022, 44.61% of the corporate credit portfolio had significant exposure to climate risk.
In addition to the credit risk assessment, the customer’s exposures are controlled to avoid over-indebtedness. Based on the client’s risk rating, size and profile, the Bank determines healthy income commitment levels (percentage of income allocated to debt servicing), as follows:
- For individuals: Overall Limits (OG) are defined to determine the client’s monthly income commitment level;
- For companies in the mass segment: the short-term monthly commitment (C), the Credit Limit (CL) and the Product Limits (PL – six product groupings according to homogeneous characteristics) are used to assess the client’s total exposure, including in the National Financial System;
- For companies analyzed on a case-by-case basis: the Risk Limit (RL) is defined separately between transactions with personal guarantee and security interest.
| Tons of CO2 equivalent p.a. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of emissions | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | △ 2022/2021 |
| Scope 1 (Direct emissions) | 639.7 | 958.9 | 728.3 | -24.0% |
| Scope 2 (indirect emissions) | 2,067.6 | 4,642.3 | 1,446.8 | -68.8% |
| Scope 3 (other indirect emissions) | 31.0 | 5,054.4 | 7,685.0 | 52.0% |
| Total emissions (Scope 1, 2 and 3) | 2,738.3 | 10,655.6 | 9,860.2 | -7.5% |
| Total Biogenic emissions of CO2 in Scope 3¹ | 13.8 | 900.3 | 1,463.4 | 62.6% |
| Other - HCFC 22 (R22) | 2,970.7 | 3,010.0 | 1,007.5 | -66.5% |
¹Considers scope 1 and 3 emissions
As for fugitive emissions, which are encompassed in Scope 1 emissions, Banrisul began a process to modernize its air conditioning equipment, in order to reduce fugitive gas emissions. In this sense, we believe it is already possible to see a slight reduction in fugitive emissions due to this program.
As for mobile combustion, Banrisul will change the fuel used by its proprietary and leased vehicle fleet to ethanol in 2023. The goal is to have the entire fleet using this fuel whenever available (given that not every gas station offers ethanol, especially when the vehicles are located in smaller cities), in order to reduce emissions from mobile combustion.
The reduction seen in emissions for reference year 2022 was due to a reduction in the reference conversion factor used by the GHG Protocol tool. In 2021, the average annual factor (tCO2/MWH) was 0.1264 and, in 2022, it was 0.0426, which explains the decrease in tCO2 equivalent emissions.
Measurement of Scope 3 emissions improved after one year. For the 2022 inventory, Banrisul included additional information in the Upstream Transport category, related to light ATM maintenance vehicles that were not included in the previous inventories. Similarly, cash and money deposit bag transportation increased significantly, in absolute number of liters of fuel used from 562,557 in 2021 to 986,962 in 2022, largely due to the gradual recovery of the economy after the pandemic.
There are no reduction targets defined, since the Bank intends to increase the number of categories included in the Scope 3, leading to an upturn in emissions.
Percentage of individuals within governance bodies by gender
| Gender | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 85.0% | 90.0% | 88.1% |
| Women | 15.0% | 10.0% | 11.9% |
Percentage of individuals within governance bodies by age group
| Age group | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 30 years old | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 30-50 years old | 32.5% | 27.5% | 26.2% |
| Over 50 years old | 67.5% | 72.5% | 73.8% |
Percentage of employees per employee category by gender
| Employee category | Gender | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superintendent | Men | 70.1% | 66.2% | 66.7% |
| Women | 29.9% | 33.8% | 33.3% | |
| Manager | Men | 61.8% | 61.1% | 60.1% |
| Women | 38.2% | 38.9% | 39.9% | |
| Analyst | Men | 62.7% | 61.4% | 60.5% |
| Women | 37.3% | 38.6% | 39.5% | |
| Assistant | Men | 55.9% | 63.5% | 55.8% |
| Women | 44.1% | 36.5% | 44.2% | |
| Without commissioned position | Men | 51.2% | 50.2% | 49.7% |
| Women | 48.8% | 49.8% | 50.3% | |
| Interns | Men | 43.0% | 43.2% | 39.5% |
| Women | 57.0% | 56.8% | 60.5% | |
| Other | Men | 53.7% | 55.7% | 54.8% |
| Women | 46.3% | 44.3% | 45.2% |
Percentage of employees per employee category by age group
| Employee category | Age group | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superintendent | Under 30 years old | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 30-50 years old | 37.3% | 32.4% | 31.9% | |
| Over 50 years old | 62.7% | 67.6% | 68.1% | |
| Manager | Under 30 years old | 2.0% | 1.6% | 1.7% |
| 30-50 years old | 68.2% | 69.0% | 69.9% | |
| Over 50 years old | 29.9% | 29.5% | 28.4% | |
| Analyst | Under 30 years old | 2.0% | 2.0% | 2.1% |
| 30-50 years old | 61.7% | 65.3% | 66.2% | |
| Over 50 years old | 36.2% | 32.7% | 31.7% | |
| Assistant | Under 30 years old | 7.2% | 2.0% | 0.0% |
| 30-50 years old | 69.7% | 68.9% | 66.2% | |
| Over 50 years old | 23.0% | 29.1% | 33.8% | |
| Without commissioned position | Under 30 years old | 7.3% | 4.2% | 2.2% |
| 30-50 years old | 67.9% | 68.5% | 67% | |
| Over 50 years old | 24.8% | 27.3% | 30.8% | |
| Interns | Under 30 years old | 86.7% | 89.4% | 88.0% |
| 30-50 years old | 12.8% | 10.6% | 11.6% | |
| Over 50 years old | 0.5% | 0.1% | 0.4% | |
| Other | Under 30 years old | 1.8% | 0.5% | 0.5% |
| 30-50 years old | 59.8% | 57.1% | 57.4% | |
| Over 50 years old | 38.4% | 42.4% | 42.1% |
Employee percentage per employee category, by color or race¹
| Employee percentage per employee category, by color or race¹ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employee category | Color or race | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Superintendent | Black | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Multiracial | 0.0% | 1.5% | 1.4% | |
| White | 100% | 98.5% | 98.6% | |
| Indigenous people | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Yellow | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Manager | Black | 1.4% | 1.5% | 1.8% |
| Multiracial | 2.1% | 2.1% | 2.6% | |
| White | 96.3% | 96.2% | 95.3% | |
| Indigenous people | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | |
| Yellow | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.2% | |
| Analyst² | Black | 2.4% | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| Multiracial | 2.2% | 2.7% | 2.9% | |
| White | 94.9% | 94.4% | 94.1% | |
| Indigenous people | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | |
| Yellow | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.2% | |
| Assistant | Black | 4.3% | 4.7% | 2.6% |
| Multiracial | 2.6% | 2.0% | 1.3% | |
| White | 93.1% | 93.2% | 96.1% | |
| Indigenous people | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Yellow | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Without commissioned position | Black | 2.3% | 2.2% | 2.0% |
| Multiracial | 3.2% | 3.0% | 2.7% | |
| White | 94.3% | 94.5% | 95.1% | |
| Indigenous people | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | |
| Yellow | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | |
| Other | Black | 2.4% | 2.2% | 2.3% |
| Multiracial | 2.8% | 3.2% | 2.9% | |
| White | 94.6% | 94.3% | 94.5% | |
| Indigenous people | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Yellow | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.3% | |
¹Interns not are not included in this calculation.
²3 analysts chose not to report their race.
As part of its commitment to the material topic, Banrisul uses renewable energy. The Bank joined the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) and the Brazilian GHG Protocol program to enhance its technical and institutional capabilities to manage greenhouse gas emissions, including calculation and reporting.
Energy efficiency and ESG in the supplier chain: the Organization has committed to managing the topic, and the quality analysis is based on regulatory compliance with Federal Law 13,589/2018.
The appropriate mapping of these processes with definition of the destination of each type of waste generated goes beyond compliance with environmental legislation, embodying the Organization’s social and environmental commitment to the community where it is inserted, and the natural resources used.
To manage energy efficiency and ESG aspects in the supplier chain, ESG criteria are used in project design, construction works and engineering services (carried out by the Construction and Maintenance departments); air quality analysis; contract management conducted by the Maintenance department; and publication of certificates to users.
At Banrisul, waste is managed by the Sustainability department, administratively linked to the Property Management Unit. This department is responsible for defining processes related to the appropriate management of solid waste produced by the Organization and for internal decision-making processes, which are validated by specific committees, when necessary.
In order to prevent and mitigate negative and potential impacts, in 2028, Banrisul implemented a Solid Waste Management Plan (PGRS, in Portuguese), which describes and recommends the appropriate handling of waste and the routine procedures necessary to comply with the legal environmental requirements.
It also controls monthly waste generation and fills out mandatory Waste Transportation Manifests (MTR, in Portuguese) with information on the transported waste, as required by the state environmental protection agency (FEPAM, in Portuguese). For each destination, specific documents are generated, such as the Waste Transportation Manifest and, at the end of the operation, the Final Disposal Certificate (CDF, in Portuguese), presenting all the information related to the waste handled.
Waste disposal processes also include concerns about stakeholders, as the disposal of certain types of waste is linked to social impact projects, including working with convicts, in the case of the decharacterization of unusable furniture, or training of vulnerable persons, as in the destination of electronic waste, through the Sustentare project, led by the Rio Grande do Sul state government, in which Banrisul has been a partner since the beginning of the initiative.
Banrisul offers its internal public distance-learning programs on sustainability and waste management, as well as in-person lectures and informational campaigns on the intranet.
One of the points identified for improving waste management processes is the update of the Solid Waste Management Plan, which will enable a review of all the incorporated practices and determine if there are gaps to be closed, as this process is conducted by a consulting firm hired for this specific purpose.
Similarly, the Bank identified the need to make the most up-to-date version of the PGRS available to the entire internal public, as well as reinforce campaigns to spread knowledge on appropriate waste sorting practices.
As an example of positive feedback from a stakeholder related to the effectiveness of waste management, there is the destination of electronic waste to the Sustentare program of the Rio Grande do Sul state government, which partners with companies, entities and associations interested in reconditioning and/or recycling electronics.
The effectiveness of renewable energy use is tracked through regular reports presented to the Administrative Officer. Energy efficiency is tracked by monitoring energy consumption at Banrisul’s premises. The air quality analysis is based on reports issued by laboratories. ESG effectiveness in the supplier chain is tracked through the inspection of the works and services with the issuance of a technical monitoring report.
Banrisul transferred consumer units to the free energy market (ACL, in Portuguese) from October to December 2022. It also delivered spaces featuring energy-efficient components and equipment, such as occupancy sensors to turn lights on and off, LED panels, inverter air conditioning equipment and sunshades. For the air quality analysis, an air collection and analysis procedure is conducted every six months at Banrisul’s premises (including both units that do and do not serve customers). Waste generation is not constant at the Organization, which makes it difficult to establish individual targets.
The Bank identified the need to have a manager that has already been hired to monitor operational and support procedures in the issuance of reports and control and track the use of renewable energy and energy efficiency. Regarding air quality, it is necessary to monitor the publication of resolutions and standards issued by regulatory and supervision agencies.
The greenhouse gas mitigation plan is designed to reduce scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions and offset all remaining emissions with the annual carbon neutral project; maintain the air-conditioning equipment at the branches within its useful life (10 to 15 years) until 2030; and sustain improvements in eco-efficiency projects. Waste management is monitored through monthly waste volume indicators, which include individual controls for each type of waste.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in the use of renewable energy | Positive | Actual | Short-term | One-time | - | During energy purchase. | Shareholders and Investors, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Energy Efficiency | Positive | Actual | Short-term | One-time | - | By purchasing inputs and hiring suppliers | Shareholders and Investors, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Incentive to ESG practices in the supply chain | Positive | Potential | Long-term | Systemic | - | In managing and operating outsourced contracts. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
The year 2022 was very important for the progress of the Diversity, Equity & Inclusion agenda, as this topic was internally institutionalized, and formal Governance mechanisms were introduced to move this work forward. To ensure diversity and collaboration that this topic requires, Banrisul created three initial Affinity Groups: Gender Equity, whose main goal is the pursuit of gender equity; People with Disabilities, with the main purpose of fostering the inclusion of colleagues with disabilities; and Race, whose goal is to promote racial equity.
To support and coordinate these Affinity Groups Banrisul created a Diversity, Equity & Inclusion Committee, composed of members from various backgrounds and the Affinity Groups’ coordinators, ensuring the necessary diversity and representativeness to address the agendas. The diversity indicators are still being developed to provide the grounds to monitor related impacts.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank’s reputation and image | Positive | Potential | Long-term | Systemic | - | Management of this topic within the Organization, from the public service exam to the termination of the employment contract. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Community, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Increase in the share of minority groups in the Organization and in leadership positions | Positive | Potential | Long-term | Systemic | - | Management of this topic within the Organization, from the public service exam to the termination of the employment contract. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Greater employee awareness of this topic | Positive | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | - | Management of this topic within the Organization, from the public service exam to the termination of the employment contract. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Development of more humane and inclusive management | Positive | Potential | Long-term | Systemic | - | Leadership development | Employees, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
The management of this topic started with the structuring of the Data and Analytics Management department, in 2019, and included the appointment of the Data Protection Officer (DPO), who is responsible for conducting internal activities to ensure compliance with the General Data Protection Act (LGPD, in Portuguese) and serve as a focal point between the Organization, the holders of personal data and the National Data Protection Authority (ANPD, in Portuguese).
The Data Privacy and Protection Governance Program was created to mitigate potential negative impacts. As part of the Program, a quarterly report is sent to the Internal Audit for compliance reporting. The Program covers several fronts, including:
• Mapping of all activities involving personal data processing, identifying the data life cycle, from collection to deletion, as well as the appropriate legal framework;
• Creation of a customer service channel for holders of personal data, ensuring the full exercise of all the rights set out in the LGPD;
• Formalization in a Standard of a flow of adaptation of contracts with third parties for compliance with the LGPD, including the definition of a methodology to help identify the Processor x Controller x Joint Controllers and define the flow for indicating LGPD clauses for business and administrative contracts;
• Implementation of the Privacy by Design and Privacy by Default methodologies in order to ensure the privacy and protection of personal data in the design of new products and services;
• Creation of specific guidelines for handling or responding to security incidents involving personal data considering the requirements imposed by the LGPD in order to complement Banrisul’s existing Information and Cyber Security Policy; and
• Development of internal training for all the staff on the main points addressed by the Law and their impacts on the workplace, as well as creation of a website featuring content that helps disseminate a culture of data privacy and protection in the Institution.
In order to address the actual negative impacts, Banrisul has approved the reporting flow of data breach incidents and created Guidelines for Prevention and Response to Personal Data Incidents. These documents are designed to ensure the prevention of personal data incidents related to Banrisul and its customers, including the means/processes that should be implemented to mitigate and/or remedy any adverse impacts thereof, as well as appropriately respond to and deal with these incidents.
To track the effectiveness of the actions, quarterly reports are made to the Audit Committee and information is provided to any internal audits. The Bank organizes an annual calendar of activities of the Data Privacy and Protection Governance Program, covering all the goals and targets for the period.
The plan is designed based on the Regulatory Agenda of the National Data Protection Authority and best market practices, taking into account sustainability aspects.The annual plan of the Privacy and Data Protection Governance Program defines indicators, which, after approved by the Executive Board, are submitted to and monitored by the Strategy and Planning department. The Program runs continuously.
Management approach
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidents with customers’ and employees’ personal data | Negative | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | Medium | In the activities or database that uses customer personal data, in the event of a failure in data security systems. | Shareholders and Investors, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Process credibility and credibility and sharing personal data | Positive | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | - | In information flow controls, through the preservation of confidentiality and integrity of information. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Greater autonomy for the holder to control personal data | Positive | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | - | Information availability, protected at all times, kept complete and available only to those entitled to access it. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Greater transparency as regards access and use of personal data | Positive | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | - | Availability and authorization to use the information only to those entitled to access it. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Community, Customers, Suppliers, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Loss of market and competitiveness due to information security incidents | Negative | Potential | Short-term | One-time | Medium | Maintenance of Information Security. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
As of 2021, Banrisul has adopted a manual that establishes sustainability criteria for procurement and bidding processes. This tool enabled the inclusion in the Organization’s procurement flow of product and service analyses related to the evaluation of the inputs used in production. As for the upstream chain, in 2022, Banrisul issued the Supplier Manual, a document with general guidelines on the Institution’s relationship with suppliers and a chapter dedicated to environmental responsibility, including guidelines on appropriate waste management at the supplier, always in compliance with the current environmental legislation.
Waste generated by Banrisul’s own activities came into the spotlight as of 2001, with the launch of the Reciclar (Recycle) program, designed to encourage and promote the environmentally friendly collection and final disposal of the waste generated by the Institution, seeking to reduce the negative environmental impact of its activities.
On the other hand, in order to reduce the generation of single-use plastic waste, Banrisul implemented Copinho Zero (Zero Cups), a project designed to encourage all employees to replace plastic cups with reusable coffee mugs and water bottles. Banrisul also has a project to streamline back-office operations in its branches with the aim to reduce the volume of paper used in the issuance of reports. Safes that are no longer used by the Institution are donated so that they can be reused. If this is not possible, they are decharacterized, and the resulting material is recycled or reused.
Electronic waste generated by the branches and units is sent to the Sustentare/RS Program, with three possible destinations: donation, reconditioning and recycling. In order to appropriately handle the furniture that the Institution no longer uses, Banrisul donates these items to non-profit institutions interested in reusing them. Banrisul also disposes of fluorescent lamps in an environmentally friendly manner by sending these components to a company hired for this purpose. In 2022, 2,734 fluorescent lamps were sent for recycling. There is also reverse logistics for materials such as batteries, structured cables and printer toner refills.
The organic waste generated by the Organization is sent for public collection in the locations where the branches are located. The waste generated by the Organization is centrally managed by Banrisul through the Sustainability Department, in particular, the waste management unit, which is responsible for managing contracts related to waste and for the receipt, temporary storage and environmentally friendly disposal of waste, through partners duly hired to handle each type of waste. Waste sent for disposal is controlled through the issuance of Waste Transportation Manifests (MTR, in Portuguese) and Final Destination Certificates (CDF, in Portuguese). All the waste destined for the Bank’s waste management is measured quantitatively through control spreadsheets and later appropriately disposed of according to the type of waste. The waste disposal is demonstrated through the issuance of Waste Transportation Manifests and Final Destination Certificates.
At Banrisul, credit risk analysis is based on statistical models for individuals and for corporate customers in the retail segment. Corporate customers in the retail segment include companies with average monthly revenue of up to R$ 1 million, which do not belong to economic groups and/or exception segments.
The exception segment is identified based on the company’s main National Registry of Economic Activity (CNAE – Cadastro Nacional de Atividade Econômica). This group includes companies that have atypical cash flows with seasonal periods, as well as those that are not targets of Banrisul’s market of interest. In the segments with low commercial interest, the Bank has listed those with high environmental and social risk.
Legal entities that are not subject to the retail analysis are also analyzed on an individual basis, in which quantitative and qualitative aspects are observed. In the qualitative analysis, besides the governance and management aspects, which are essential for credit risk analysis, environmental and social matters related to the company and its production chain are evaluated. These analyses are performed by risk analysts, who are arranged in specialized groups per sector in which the companies operate, who interact with each other and have an in-depth knowledge of the companies, their role and impact on the local economy – a situation that provides an opportunity for a better identification of possible risk factors and atypical behavior by some companies. Also, for large corporations, risk assessment is carried out based on specific qualitative aspects for approaching ESG topics, which result in a classification that takes into account these aspects without being limited to them.
The retail risk analyses are carried out based on the information recorded in our registration, billing, and incident reporting (BLT in Portuguese) systems. The BLT system gathers have internal and external incidents received from credit bureaus and other official bodies, registering managerial and restrictive incidents that may indicate the worsening of risk from the ESG perspective, among them is forced labor and environmental damage, both considered as impediments to credit assignment. As for individual analyses, in addition to these same controls, data extracted from the financial statements and notes thereto, as well as other information made available by customers are used. They must also fill out a specific checklist, which helps analyst to gather qualitative information that will be used in their opinion, including risk analysis and exposure limits.
Risk analysis for the formation of exposure limit is generalist, that is, it addresses the most relevant information and considerations for credit risk without yet considering the specific characteristics of the credit that will be contracted. Within this context, additional information and analyses may be requested during the analysis and operations are approved observing ESG aspects, with special relevance for investment lines, agribusiness and real estate ventures.
Given the relevance of credit exposures, all operations above R$10 million in which the use of funds or directed credits is known must fill out a questionnaire (Formulário Normatizado Modelo 1.31000.01). The questionnaire may also be applied to other operations or amounts lower than this threshold.
Allowance for loan losses (PCLD in Portuguese) is calculated monthly for all active contracts based on the rating calculation. Currently, the customer not having an approved credit exposure limit is one of the factors that can worsen the rating classification of Banrisul’s credit operations. For some industries, this individual analysis to determine exposure limit is forbidden, for example sectors/CNAE of gambling and betting, several agricultural crops (such as tobacco and sugar cane).
Moreover, the analysis of denials of exposure limits may occur due to the lack of environmental licenses, debts with the union, and one of the consequences is the possibility of worsening the rating classification, especially for customers who already have exposure with the Bank.
Furthermore, regardless of the exposure limit in force and the size of the company or individual customer, in the monthly calculation of the Allowance for Loan Losses, incidents are verified that may worsen the customer’s risk in a timely manner, such as inclusion on the Forced Labor list, Court Restrictions, internal audit notes for fraud, fraud with the Bacen and irregularities with the Brazilian Securities and Exchange Commission.
ESG aspects are assessed qualitatively by the credit risk analysts and the evaluation is in line with Banrisul’s Institutional Manual/ Social and Environmental Responsibility Policy.
Considering that the individual analyses rely on relevant information from the ESG agenda, but are not limited to it, the experiences gathered in the course of these analyses, together with the ongoing monitoring of trends, are currently how the institution identifies opportunities for improvement in our processes.
In monitoring the credit portfolio, Banrisul has viewed credit allocation according to the sector in which the customer operates, as well as the largest individual exposures and those of economic groups. These views are shared with various Banrisul units, contributing to timely initiatives that may lead to adjustments in the automated exposure limits – an action carried out with greater recurrence during the pandemic, in individual analysis of the exposure limits (LR), in adjustments to the parameters of Allowance for Loan Losses calculation or in the worsening of the company’s risk rating – via individual analysis (monitoring) .
In the geographic context, the statistical models used in credit assignment have a variable that signals the main regions of the state where the information is gathered by the customer relationship branch, which, together with the CNAE (corporate customers) or CBO (individuals) information, add to and complement this sector and geographic evaluation.
In addition to the statistical models used for credit risk assessment, which aim at mitigating the risk of default and supporting the credit assignment process, the customer’s exposure is controlled in order to avoid over-indebtedness, which, based on the customer’s risk rating, size and profile, seeks to outline healthy levels of commitment, such as:
– For individuals, Global Limits (LGs) are outlined that mark the level of monthly commitment of the customer’s income;
– For corporate customers in the retail segment, there are the short-term monthly commitment (C), the Credit Limit (LC), and the Product Limits (LP – grouping of products according to homogeneous characteristics) – assessing the customer’s total exposure, including in the National Financial System;
– For legal entities that have individual analysis: Risk Limit (LR) is defined divided between operations with personal guarantees and those with real guarantees.
Also, statistical models are used for individual customers to classify the levels of vulnerability. Vulnerability is assessed in order to mitigate the risks related to the customer’s understanding (or lack of understanding) regarding products and services, as well as the risk of over-indebtedness. In order to qualify the service to customers with higher risk arising from their vulnerabilities or classified at a high level of vulnerability, their credit operations are analyzed exclusively by a higher committee.
In relation to customers who are circumstantially in financial vulnerability, the Bank has specific conditions and credit lines to readjust their financial flows, aiming to preserve Banrisul’s interests – both in receiving the credits granted and in satisfying the customer’s interest – to reorganize their flows and readjust their responsibilities to the Bank.In addition to these customer-focused aspects, the business areas make products focused on sustainability available. There is also a specific policy that establishes criteria for the acceptance of guarantees, which are aligned with the best market practices.
Banrisul is committed to investing in the regional culture and development, therefore, it seeks to support cultural and sports projects in the state’s different regions. Projects are assessed considering their relationship with regional development and their practical extension in several social aspects. These initiatives impact the local community through the economic development and accessibility improvements and contribute thought the preservation of tangible and intangible cultural heritage, in addition to fostering Rio Grande do Sul’s innovation ecosystem. As regards sports and education, projects offer better access to education, encourage young people and children to take up sports and contribute to fostering citizenship, human development and respect for equality in the population of Rio Grande do Sul.
Initiatives to improve the access to financial services for disadvanteged people
| Target disadvantaged group | Degree to which it is applied across the Institution | Progress made towards the initiative |
| Persons with disabilities | Process of mapping and improving the granting and renewal of technical opinions, declaring the correct application of pertinent to Architectural Accessibility of the buildings, in the case of Banrisul Branches, mainly in compliance with NBR 9050/2000. | Process started at the end of 2021. |
| People with Visual Impairments | Development of improvement in the voice communication systems in all Banrisul's most recently acquired ATMs, complying NBR 15250/2005. | Process started in 2019 and is currently in approval phase |
| People with Visual Impairments | As of 2018, audio description resources have been applied to Banrisul Group’s main websites to allow accessibility in compliance with the Brazilian Inclusion Law, SARB 01 - W3C Accessibility. | The description of images is already mandatory when posting pictures on the websites of Corretora de Valores, Consórcio Banrisul, BAGERGS, Novo seja Vero, Banricard and the Promotional Website. This is being implemented on the Banrisul Portal. |
| Persons with Disabilities | Since 2014, the Bank has continued to install the Accessible Desk, which is adapted/lowered furniture for priority/preferential service in all Banrisul branches, especially designed for wheelchair users or people with dwarfism. Compliance with Decree Law 5296/2004. | Monitored in 2021, in compliance with the regulation. |
| People with hearing impairments | Since 2008, Banrisul has trained employees to ensure they know the Brazilian Sign Language (Libras) to provide services to deaf and hard of hearing customers in its branches. The initiative complies with current regulations. | In 2021, the Bank recorded 1,296 trained employees, seeking to have at least two employees that know Libras at each of its branches. |
| People with Visual Impairments | As of 2018, Banrisul started to make the Debit and Credit Card Kit available to all its visually impaired customers. In addition to the traditional plastic card, the kit has information in Braille System and in Enlarged Font. | Every visually impaired customer duly registered at BAL already receives the card with tactile or visually enlarged accessibilities. More than 2,000 debit cards have already been issued from a base of about 1500 customers. |
| Persons with Disabilities | In 2014, the Bank launched the Accessibility distance learning program geared towards informing about the people with disabilities group and informing the staff about the best service practices and resources that can be offered to people/customers with disabilities or reduced mobility at Banrisul, with the aim of ensuring the inclusion of this public in the banking universe. The program seeks to comply with the regulations on Priority Service. | Approximately 30% of active employees had already taken the course in 2021. |
| People with visual impairments | The Banrisul Digital app has been following all the rules and development protocols to ensure accessibility to people with visual impairments, complying with SARB 01 and best market practices. | The Banrisul Digital Application is being developed so that all the services that have been or will be implemented have 100% accessibility in both IOS and Android systems. |
The credit policies definitions are available in internal regulations and are also parameterized in the “Customer Registration”, “Negative Incidents” and “Risk Calculation” systems. The Bank currently checks with external agencies whether the customer, either an individual or a company, has been listed as an “Employer that uses Forced Labor” or as causing “Environmental Damage” (conviction for environmental damage in actions filed by Brazil’s environmental protection agency (IBAMA, in Portuguese)).
Customers identified as “Employer of Forced Labor” are prevented from contracting any type of credit operations. We also monitor customers who already have a relationship with us and who may be included in those lists, taking specific actions to discontinue the business relationship.
Banrisul is committed to investing in culture, education, sports and technological innovation in order to promote social and economic development in small towns and large cities in Rio Grande do Sul. In this sense, through sponsorships and donations, it supports cultural, educational and sports projects, in addition to hundreds of fairs, shows, and exhibits on family farming, agriculture, livestock, industry, regional tourism, food and technology, among others.
The projects are evaluated considering their relationship with the various social, cultural and economic aspects of the communities and regions, understanding their potential, interests and needs, and seeking to promote integration and sustainable regional development.
In 2022, Banrisul sponsored more than 200 projects in several areas, distributed in almost 200 municipalities in Rio Grande do Sul, comprising fairs, shows and exhibits on agriculture, livestock, family farming, food and rural development; municipal and regional fairs, shows and exhibits on agriculture, livestock, industry and commerce; and cultural and sports events, music and folklore shows, book and tourism fairs, among other activities involving the public and private sectors. The targets for 2023 include the implementation of the objectives of the Sponsorship Call, with support for 345 selected projects. In addition, a second Call for Proposals is planned for the year.
List of material topics:
- Innovation and technology;
- Corporate governance and integrity;
- Data privacy and security;
- Sales practices and customer satisfaction;
- Sustainable products and business;
- Partner and supplier management;
- Human capital development;
- Eco-efficiency;
- Diversity and Inclusion;
- Financial inclusion and education;
- Environmental, social and climate risk strategy.
Compared to 2021, the following new topics were added to the materiality list: “Diversity and inclusion”, “Corporate governance and integrity”; “Data privacy and security”; “Partner and supplier management”, “Human capital development”, “Eco-efficiency” and “Financial inclusion and education”.
In 2022, the topics “Risk approach and opportunities related to climate change” and “Quality of customer service and services provided” were added to the “Environmental, social and climate risk strategy” and “Sales practices and customer satisfaction”, respectively. The topic “Management of risks that can significantly impact business” was also added to “Environmental, social and climate risk strategy”.
Furthermore, topics “Management of energy consumption and solid waste generation”, “Criteria for financing assignment, positive impact and delinquency”, “Social investment in the external community” and “Business expansion strategy” have been excluded in this new step.
Since 2001, Banrisul has the Reciclar (Recycling) Program, aimed at encouraging and fostering environmentally friendly waste collection and recycling at the Institution, in line with the environmental legislation in force.
Recyclable waste (unserviceable paper, metals, plastics, glass, among others) are treated differently, according to their classification. Paper and cardboard are sent to recycling through partners that receive this material and properly dispose it. In 2021, 206.6 tons were sent to partners.
Metals are sent to a specialized partner in the steelmaking industry for subsequent recycling. In 2021, 114.1 tons of metal scraps were sent for recycling. For the institution’s unserviceable safes, Banrisul seeks to donate them to be reused. When this is not possible, they are sent for decharacterization, so that they can be recycled or the materials resulting from this process can be reused. In 2021, 16 units of safes were sent for proper disposal (donation or recycling), totaling 10.4 tons of these items.
With regard to plastic waste, Banrisul has been implementing the Copinho Zero Project to replace the plastic cups used by employees with mugs and squeezes, which will result in a significant reduction in the generation of this type of waste in the organization’s premises. Banrisul estimates that by the end of 2022 disposable cups will no longer be used, leading to a decrease in plastic waste generation.
Banrisul is concerned about the disposal of acrylic waste, which is sent to a partner that uses it as raw material, allowing its reinsertion in the production chain. As for electronic waste, the volume generated by the branch network and units is properly disposed of through the Sustentare/RS Program which, in turn, uses three destination options: donation, reconditioning and recycling. Accordingly, in 2021 alone, through this program, Banrisul directed 93.4 tons of electronic equipment to proper disposal.
Seeking to promote the reuse of unserviceable furniture, the Bank donates these items to non-profit institutions that want to reuse them. In 2021 alone, 4,999 furniture units were donated to charitable institutions such as schools, APAEs, and the Military Police. In turn, the furniture that cannot be donated is sent to institutions that dismantle and reuse the material for other purposes, such as, for example, Banrisul’s partnership with the State Penitentiary of Canoas in which the inmates transform the furniture into houses for animals, which are then installed in public places across the city.
Banrisul also properly disposes of fluorescent lamps by directing these components to a company hired for this purpose. As regards fabric and canvas scraps, the Bank has partnerships for their proper disposal, through co-processing, in which waste will be used as fuel for the cement industry’s furnaces.
The organic waste generated by the organization are directed for public collection in the cities where the branches and units are located. A company has been hired for the disposal of organic waste at the administrative headquarters building.
In terms of procurement, in 2021, Banrisul added sustainability standards in the purchasing and bidding criteria, in order to use them as conditions for purchases that are increasingly in line with social, environmental and climate matters.
The waste generated by the organization is managed centrally by Banrisul, through the Sustainability Corporate Department, which is responsible for receiving, sorting and disposing of waste in an environmentally correct way, relying on duly accredited partners for each class of waste.
All waste directed to the Bank’s waste management are qualitatively and quantitatively measured through control spreadsheets, and later, according to the type of waste are directed to the proper disposal. Therefore, waste disposal is monitored by issuing the Waste Transport Manifest (MTR in Portuguese) and the Waste Final Disposal Certificate (CDF in Portuguese).
All employees receive training on the Code of Conduct and Ethics and on Anti-Corruption. Banrisul has other institutional policies and makes a whistleblowing channel available both on the internal and external websites.
Banrisul’s Whistleblowing Channel is a communication tool that allows employees, customers, users, partners or suppliers to report possible misconduct of any nature related to the Institution’s activities that affect its reputation and violate its internal controls and Banrisul’s Compliance Program.
The Whistleblowing Channel recorded stable figures in 2018 and 2019, receiving 155 and 153 reports, respectively. In the following years, the number of reports spiked significantly to 536 in 2020 and 433 in 2021. This increase had two main reasons: first, the Institution made a channel available to external stakeholders, offering more visibility, thus increasing the number of reports; and second, the pandemic, which altered the service routine at the branches, leading Customers to use this channel to request information from the Bank.
In 2022, there was a significant reduction, only 234 contacts were made, reflecting the acculturation of the correct use of the channel.
[wpdatatable id=261
Number and rate of new employee hires by age group
| Number and rate of new employee hires by age group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||
| Under 30 years old | 129 | 57.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% |
| 30 - 50 years old | 88 | 39.1% | 3 | 50.0% | 9 | 69.2% |
| Over 50 years old | 8 | 3.6% | 3 | 50.0% | 4 | 30.8% |
| Total | 225 | 100% | 6 | 100% | 13 | 100% |
Number and rate of new employee hires by gender
| Number and rate of new employee hires by gender | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||
| Women | 58 | 25.8% | 2 | 33.3% | 2 | 15.4% |
| Men | 167 | 74.2% | 4 | 66.7% | 11 | 84.6% |
| Total | 225 | 100% | 6 | 100% | 13 | 100% |
Number and rate of new employee hires by region
| Number and rate of new employee hires by region | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||
| South | 225 | 100% | 6 | 100% | 13 | 100% |
Note: In 2019, employees approved in the 2018 public service examination continued to the called, therefore the low rate of new hires in said year. In 2020 and 2021, advisors and an Officer were hired, and former employees were hired.
Note: Turnover rates by age group, region and gender were approximately 0% in 2019, 2020 and 2021.
As of November 2021, 100% of suppliers have been hired considering sustainability criteria. These criteria include the use of Forest Stewardship Council® (FSC) labeled paper sheets, equipment with lower impact on ozone emissions, and the proper disposal of construction waste.
After Sustainability department has been implemented, hired suppliers began to have a direct vision of the respective criteria to which they have adhered, and the trend is to increase the percentage of suppliers that value environmental criteria through the work developed by the department.
No administrative proceedings originating from discrimination on any grounds, whether of race, color, sex, religion, etc., were identified in 2021.
After the creation of the Sustainability department, all contracts started including analyzed environmental criteria, which are analyzed and defined according to the scope of each contract. As contracts may have specific sustainability criteria, such as the use of sheets with the FSC seal, equipment with lower impact on ozone emissions and appropriate disposal of construction waste, among others, it is estimated that all contracts signed by Banrisul go through an analysis of environmental criteria.
The Bank’s occupational health and safety management system is guided by a broad set of actions and initiatives that mainly comprise the Environmental Risk Prevention Program (PPRA, in Portuguese) and the Occupational Health Medical Control Program (PCMSO, in Portuguese). It is important to note that after the update of NR-01 and NR-09, as well as the publication of Ordinance no. 8.873, as of January 2022, PPRA will be replaced by the Risk Management Program (PGR in Portuguese).
The Internal Commission for the Prevention of Accidents (CIPA, in Portuguese) and specific technical documents, e.g., the Social Security Professional Profile (PPP, in Portuguese) and the Technical Report on the Work Environment Conditions (LTCAT, in Portuguese), as determined by the legislation, complement the system. As regards specific employer initiatives included within the main scopes, a protocol for fighting the Covid-19 pandemic has been implemented, in addition to the Alcohol and Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment Program (PAD, in Portuguese), Occupational Diseases and Work Accidents Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment Program (PROAT, in Portuguese) and the Program for Attention and Monitoring of Employees in Stressful Situations (PASS, in Portuguese). As for Ergonomics, employees are evaluated and receive individual guidance and their workstations are adjusted, according to demand.
The Occupational Health Medical Control Program (PCMOSO in Portuguese) provides the guidelines for the company’s health initiatives and ensures compliance with occupational medical examinations, contributing to the early identification of occupational illnesses and referring these employees to specialized treatment when necessary. The program’s quality is monitored longitudinally throughout the year through the health records generated, and all medical records are managed, evaluated and filed by the Specialized Safety Engineering and Occupational Medicine Service (SESMT in Portuguese) team. In order to make the user’s access easier, the exams are preferably performed in loco at the branch network, avoiding travel inconveniences and, at the same time, enabling an organizational assessment of the work environment by the hired professional. This scope covers only Banrisul employees. Regarding outsourced workers, the service is implemented by the contractor’s SESMT.
Banrisul has a sponsorship project designed to support projects in the areas of culture, sports, social responsibility, education and technological innovation with a focus on serving the interests and meeting the needs of the target audience. The projects are designed to expand access to capacity building and cultural activities and equipment, thus promoting, in addition to knowledge and experience to young people and adults, job creation and income generation, opening up opportunities and contributing to the promotion of citizenship, human development and respect for equality. By supporting these projects, the Bank is integrated into the communities, seeking to help transform and improve the quality of life of part of the local population.
The bidder is responsible for analyzing the direct environmental impacts of the event; however, the project analysis stage takes into account aspects such as sustainability, social responsibility and citizenship, democratization and others. Any bids that cause damage to the environment or involve cruelty to animals will be disqualified.
In 2022, Banrisul sponsored more than 200 projects in several areas, distributed in almost 200 municipalities in Rio Grande do Sul, comprising fairs, shows and exhibits on agriculture and livestock activities related to industry, commerce and family farming on a municipal and regional scale, in addition to cultural, sports events, music and folklore events, book and tourism fairs, and other activities involving the public and private sectors.
The goals for 2023 include the fulfillment of the objectives of the Call for Sponsorship Proposals, with support to 345 selected proposals. In addition, a second Call for Proposal is scheduled for the year.
According to Banrisul’s Anti-Corruption policy, all those subject to it are responsible for fostering an ethical culture and for creating an environment of permanent control and prevention of corruption, in which it is possible to monitor and identify, through Due Diligence procedures, operations from customers and non-customers, individuals and legal entities, as well as actions or suspected corruption crimes, as well as enforcing the internal integrity and auditing mechanisms and procedures, encouraging whistleblowing and the effective application of this policy and Banrisul’s Code of Ethics and Conduct.
Moreover, in 2021, a social and environmental risk assessment questionnaire was developed for operations over R$10 million.
The Bank is subject to both foreign and Brazilian anti-corruption laws. These laws require the adoption of integrity procedures in order to mitigate the risk that any person, acting on behalf of the Bank, may offer an undue advantage to a public agent, in order to obtain benefits of any kind. The transnational scope legislations, including, but not limited to, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977 and the UK Bribery Act of 2000, in addition to Federal Law no. 12.846/13, provide for the adoption of specific policies and procedures for the prevention and fight against illegal acts related to corruption of public administration entities and government representatives, which aim at ensuring any kind of advantage. They also require the Bank to keep its books and records accurate and rely on an internal controls system to certify their respective veracity, in addition to the prevention of illegal activities.
Through sponsorships, Banrisul strives to be part of society by fostering projects that, preferably, contribute to employment and income generation. Such projects are linked to culture, sports, social responsibility education and technological innovation, and their achievements are of public interest, so as individuals and the community are positively impacted. In turn, the Bank’s brand is associated to social and environmental projects, which contribute to a broad disclosure to the population.
Climate change management at Banrisul includes transition and physical Climate Change Risks, as defined by CMN 4,943/21:
Transition climate change risks: possibility of the Institution incurring in losses arising from events associated with the transition to a low carbon economy;
Examples of transition climate change risks include legal and regulatory changes; technological innovations; changes in products and services supply and demand; unfavorable perception from clients the financial market or society in general; events related to the transition to a low-carbon economy and that negatively impact the Institution;
Physical climate change risks: possibility of the Institution incurring in losses arising from events associated with short and medium-term frequent and severe weather events or long-term environmental changes that can be related to changes in climate patterns.
Climate risk events can lead to financial and reputational losses, as well as to process inefficiencies. Possibilities of losses associated with the other types of risks to which the Institution is exposed, especially operational and credit risks, can be identified.
In addition to monitoring the regulatory environment and customer perception, management includes consulting information on public lists and verifying the activities, products and services subject to social and environmental legislation. As for the operations, Social, Environmental and Climate Risks inherent to the activity’s economic industry are identified, based on the National Registry of Economic Activity (CNAE – Cadastro Nacional de Atividade Econômica) code). Climate risk management costs are not calculated individually, but are considered together with the resources allocated to the Institution’s risk management.
Banrisul’ participates in Febraban’s committees and squads, in AMCHAM’s ESG Committee and the Interinstitutional Committee on Environmental Education (CIEA in Portuguese).
The Bank does not use the positive screening criterion for Development Lines; however, the approach used excludes companies that are not in compliance with it, whether environmental or labor, and takes into account the applicable legislation and the requirements of the onlending agents (BNDES, FINEP and FGTS). Thus, the borrower’s legal, social and environmental compliance is monitored by the competent technical area. As for social and environmental criteria, Banrisul has adopted the practice of not granting credit to companies that carry out activities that do not comply with the proper environmental agency, i.e., companies that do not have an environmental license. If the borrower is included in the Ministry of the Economy’s list of employers that submit their workers to degrading forms of labor or keep them in conditions similar to forced labor is also considered a restriction for credit approval.
In order to mitigate social and environmental risks throughout the operation’s effectiveness, the Bank relies on contractual clauses for extraordinary or early maturity for cases of non-compliance with legislation, problems with environmental licensing, crimes against the environment, forced and child labor. There are no exclusions or limitations to audit coverage related to regions or products and services.
The Company does not have a specific sustainability policy for rural credit; however, it complies with state and federal environmental legislation for contracting these transactions. Moreover, Banrisul follows the rules set out in the Rural Credit Manual that addresses social and environmental compliance, which must be verified during the proposal stage, before credit is granted, and during the effectiveness of the contract. Internal credit standards should also be followed. Banrisul’s Social, Environmental and Climate Risk Management Policy and Social and Environmental Responsibility Policy are also complied with.
Banrisul carries out the continuous and integrated management of capital and credit, market, interest rate variation risks for the instruments classified in the banking portfolio – IRRBB; as well as liquidity, operational, social, environmental, climate and other risks considered relevant. Social, Environmental and Climate Risks (RSAC, in Portuguese) are some of the various types of risk to which the Institution in exposed and must be managed in an integrated manner with the other corporate risks.
The Social, Environmental and Climate Risk management structure includes the assessment of Stress Testing results, the monitoring of the risk indicators defined in the Risk Appetite Statement (RAS) and the periodic preparation of reports. In regard to Stress Testing, the Social, Environmental and Climate Risk is included in the other corporate risks since its impacts are mostly observed in credit and in civil and labor lawsuits.
Geared towards meeting the new requirements, Banrisul has developed action plans, which are being implemented and will improve the governance, analysis, management and reporting of social, environmental and climate risks.
When offering a new product, service, or solution, the Bank carried out an analysis to verify potential risks to public health, the environment, infringement of laws and regulations for social and environmental protection, contributing to or being affected by changes in climate patterns.
There is no specific sustainability policy for rural loans in the agribusiness sector, however, the legal obligations and the guidelines of the Rural Loan Manual, which addresses environmental and social compliance in credit assignment, must be followed. Products managed comply with the Bank’s credit and sustainability policies, in addition to the guidelines of onlending agents, always complying with new sustainable aspects. Accordingly, the Company relies on the Responsibility Policy (PRSAC in Portuguese), which guides the practices, processes and business, coupled with the Management of Social, Environmental and Climate Risks.
Training Program – Business Managers and Business Managers from Other States
The program trains and develops professionals to work at the branch network serving corporate customers. Its contents are focused on developing commercial and technical skills desired in a future Business Manager, such as negotiating products and services; prospecting, attracting, and following up customers through efficient tools and approaches, thus optimizing their business actions.
Training Program – Account Managers
The program promotes the integration, training and development of the employees selected to work in the new Account Manager position, developing the required skills and attitudes for performing their activities well, with emphasis on the development of interpersonal competencies focused on preparing them for building a relationship with high-income individual customers.
Training Program – Business Operators
The program trains employees selected to work in the new Business Operator position, aiming to prepare professionals to serve and address the Bank’s Individual Customers. Its contents include specific technical knowledge with efficient tools and approaches to optimize business with customers.
Training Program – Supervisors
The program prepares and develops professionals to work as Supervisors in the branch network, serving the Bank’s internal and external public. It develops and enhances basic, technical and job-related skills, as well as skills related to other positions in the bank and managerial ones, focused on planning, organizing and executing the position. Aligned to the Bank’s Strategic Planning, it aims at achieving administrative and commercial goals.
Training program – Market Managers
The program trains and develops employees selected for the new Market Manager position in the branch network, to work serving the Bank’s Corporate and Individual Customers. The program enhances and develops technical and behavioral skills, focused on negotiating, prospecting, attracting and following-up with customers. Training Program for Agribusiness Relationship Managers.
Training Program – Agribusiness Relationship Managers
These professionals will manage a pre-established customer portfolio of the respective banking stations at the Suregs, focused on medium- and high-income rural produces. This position aims to serve a customer niche who demands special and exclusive treatment.
Training Program – Agribusiness Managers
The program prepares employees selected for the new Agribusiness Manager position, developing technical skills focused on the agribusiness segment, expanding their knowledge of rural credit products and services, aiming at attracting and managing new business in this segment.
Training Program – Corporate Business Managers
The program aims to train professionals to manage large companies. It is important to note that this position serves a customer niche who demands special and exclusive treatment.
Training Program – Government Business Managers
The Training Program for Government Business Managers aims to prepare professionals to work at the superintendencies, in line with the Government Business Unit’s goals.
GRI 404-2
| Participants in training programs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Training program | Total participants | |
| 2021 | 2022 | |
| Managers¹ | 138 | 175 |
| Business operators | 70 | 202 |
| Supervisors | 0 | 11 |
| Total | 208 | 388 |
¹ It includes business managers in the categories: corporate, other states and government; account managers, market managers, and agribusiness relationship manager.
GRI 404-2
| Distance Learning - Banrisul | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance Learning - Progress of courses offered over the past years | |||
| Distance learning training hours | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Students enrolled | 128,376 | 303,415 | 412,801 |
| Employed on December 31 | 34,367 | 89,760 | 151,280 |
| Average training hours per employee | 9,280 | 9,002 | 8,658 |
| Number of classes offered in the platform | 13.8 | 33.7 | 47.7 |
| Distance learning training hours | 1,420 | 1,869 | 2,734 |
Career transition assistance programs focused on facilitating continued employability and end of career management due to retirement or termination of employment contract – specially for retired employees are not being offered at the moment. As regards continued employability, the Bank follows-up with the participants of the Pescar Project and the Young Apprentice Program in order to monitor their insertion in the job market after completing their experience at Banrisul.
TRAINING PROGRAMS: The aim of the training programs is to develop and prepare employees for professional development. Each program is designed according to its specificities, in line with the employee’s professional development and Banrisul’s business strategies. The knowledge shared, the theory allied to practice, the experiences, the corporate games, the interpersonal relationships, the participation of department heads and the dedication of the instructors make the programs unique experiences in the preparation of professionals who will take over strategic positions in the Bank. In 2021, still in the online format, 150 professionals received training, with two Business Manager classes, one Agribusiness Manager class, one Agribusiness Relationship Manager class, one Government Business Manager class, two Account Manager classes, two Market Manager classes, and three Business Operator classes. By May 2022, 131 professionals had already been trained.
WEBINARS – TÁ NA PAUTA AND CONTINUING EDUCATION: It aims to share experiences among professionals who have already gone through the training programs, geared towards expanding possibilities for business strategies and results. In 2021, 224 employees participated in six webinars, totaling 1,217 training hours.
FRAUD PREVENTION ON BANKING DOCUMENTS: The program aims to meet the Brazilian Central Bank (Bacen in Portuguese) and the National Institute of Information Technology (INTI in Portuguese) requirements, reducing the historical impact of losses on financial institutions, which increased from 30% to 54%, up by 80%. In 2021, 136 cashiers have been trained on the Bank’s cybersecurity platform and 20 young people participated in Banrisul’s Projeto Pescar, totaling 156 training hours.
EXTERNAL COURSES (COURSES, LECTURES, EVENTS, SEMINARS, CONGRESSES, ETC.): Banrisul identifies the needs for improvement or demands from its Units and Regional Superintendencies and makes open courses, lectures, seminars, congresses and other initiatives focused on professional qualification available to its employees. In 2021, 1,576 people participated in 176 external events, totaling 41,949 training hours. By May 2022, 1,040 people participated in 74 external events, totaling 4,988 training hours.
INTERNAL SEMINARS AND WEBINARS – NETWORK AND GENERAL MANAGEMENT: These seminars and webinars meet the General Management’s Units and Branch Network demands for specific webinars, seminars and workshops, seeking to share knowledge about products and services, commercial strategies and guidelines, sales campaigns, launch of new products/services or updates, changes to legislation, as well as other relevant topics that are in line with the strategic planning. In 2021, 12,457 employees participated in 92 events, totaling 43,782 training hours, and, by May 2022, 4,037 people attended 27 events, totaling 4,905 training hours.
FIRST MANAGEMENT PROGRAM: A course aimed at professionals selected to take over the position of General Managers or Associate Manager. The program was designed to develop competencies, skills and attitudes required for a good performance on the new position, focusing on administrative-operational management, people and business management, besides focusing on the development of a systemic and strategic view of the Bank’s various products, services and processes. In 2021, 50 professionals participated in the program, totaling 1,200 training hours.
MENTORING PROGRAM (MODULE INCLUDED IN THE FIRST MANAGEMENT PROGRAM): Program geared towards training and qualifying the new general and associate managers in the best management practices. This program aims to train mentors, experienced professionals or those with specific expertise to mentor employees who are developing their careers or in professional growth at the Bank. In 2021, 50 professionals participated in the program, receiving mentoring from two superintendents, two general managers and two associate managers.
LIBRAS (BRAZILIAN SIGN LANGUAGE): Course developed in compliance with Bacen Circular Letter No. 3,369 of 10/19/07, which “provides for proof that financial institutions and other institutions authorized to operate by the Brazilian Central Bank are in compliance with the accessibility requirements set forth by Decree no. 5.296, of 2004”, as well as to meet the “Consent Decree” (TAC in Portuguese), including the Training in the Brazilian Sign Language. In order to comply with this resolution, since 06/29/2010, the Bank seeks to, through the Corporate University, train two employees per branch in Libras – one as a teller and the other working on the service platform. The program’s goal is to provide basic and refresher training courses in Libras for employees of the branch network, with a specific focus on banking services for hearing-impaired customers. The forecast for 2022 is to train another 240 employees. There are currently 1,282 professionals in the Banrisul staff trained in Libras.
INCENTIVE TO HIGHER EDUCATION: This program includes Undergraduate, Graduate, Master’s and Doctorate degrees offered by higher education institutions authorized to operate by the Ministry of Education and Culture (MEC in Portuguese).
The program aims to help employees who are undergraduate, graduate, master’s and doctoral students by providing financial support to cover education expenses, taking into account that a better qualified employee results in improvements to the organization’s processes and strategies. In 2021, the total amount reimbursed was R$1,121,882.65 for 309 employees, of which R$ 254,396.42 in 206 Undergraduate programs and R$867,486.23 in 103 Graduate, Master’s and Doctorate programs.
By May 2022, R$ 168,762.20 had been reimbursed to 59 participants, of which R$58,642.88 in 52 Undergraduate programs and R$110,119.32 in seven Graduate, Master’s and Doctorate programs.
INCENTIVE TO LANGUAGE LEARNING: It includes language courses offered by educational institutions or private teachers, by free choice of the employee. During 2021, R$99,481.06 were reimbursed to 189 employees and, by May 2022, R$40,641.07 were reimbursed to 68 participants.
INSTRUCTOR PROGRAM: It was designed to train internal instructors who work in the Training Program, raising the quality of the corporate education programs, so that skills are gained, and learning is applied in practice. In 2021, 56 employees participated in the Instructor Training course, totaling 4,480 training hours, and also 22 employees attended in the online Instructor Qualification course, totaling 220 training hours.
APRRECIATION AND USE OF ACADEMIC RESEARCH: The Bank identified the need to more assertively bring its different knowledge areas and departments closer to the research and final papers of employees. Thus, Banrisul intends to establish a channel whereby academic research can be validated, has greater applicability and is supported by precise information from the technical departments, while at the same time all the knowledge, innovation and discussions in academia can converge and result in improvements to Banrisul’s processes, products and services. Other stakeholders can also conduct academic research at Banrisul, including employees without incentive, interns and external stakeholders. In 2021, 211 academic research workflows were received, which were connected to the units that appoint the facilitators according to the topic of the final paper.
AGILE METHODS: Training that aims to spread the culture and encourage the development of the Bank’s administrative employees towards an innovative and agile environment. In 2021, 216 employees participated in the program, totaling 2,728 training hours.
Banrisul Distance Learning: Based on the Units’ and the Branch Network’s demands, as well as on the needs identified according to the Bank’s strategy, e-learning materials are developed, or courses are acquired to supply the Distance Learning platform.
Programs for upgrading employee skills and transition assistance programs
| Distance Learning - Progress of courses offered over the past years | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance Learning at Banrisul | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Distance learning training hours | 128,376 | 303,415 | 189,405 |
| Students enrolled | 34,367 | 89,760 | 64,392 |
| Employed on December 31 | 9,280 | 9,030 | 8,840 |
| Average training hours per employee | 13.83 | 33.60 | 21.43 |
| Number of classes offered in the platform | 1,420 | 1,869 | 1,082 |
¹By May 2022
HORIZONS – TELLERS’ REALLOCATION PROGRAM:
The program aims to train and develop professionals that used to hold the position of “bank tellers.” The process of reallocating employees who work at the teller position involves two main stages and three complementary ones, according to the Bank’s needs. The first stage is the awareness-raising (of both tellers and managers), that is, the possibility of preparing for change in position. The second stage is focused on basic training, enabling the employee to work on the branches’ main demand: customer service with a commercial focus. The third stage consists in providing specialization courses for the professional to work focused on Agribusiness, Credit Recovery, Corporate Service, and others, according to the Bank’s strategy. In 2021, the Bank held training webinars and referred distance learning courses that could be taken according to each employee’s specialization and together with their respective responsibilities at the branches.
PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM:
The program aims to assist and provide tools to professionals who are underperforming in one or several indicators, in order to create an action plan together with the employee, according to their position, providing the necessary support performing their activities. The program includes distance learning courses, supervised activities, and mentoring. Participants are indicated by HR department – Personnel Management/ Monitoring, according to the Branch System’s Performance Assessment policy, in which the employees not classified in the ranking must go through a ‘performance rescue’ process, under the supervision of the regional superintendency, including some of the listed actions. In 2021, three employees participated in the program, totaling 12 training and mentoring hours.
For non-work-related health demands, the Institution offers Cabergs, a self-management health insurance plan, to all its own employees, who have to option to join it or not. Covered services are spread across several regions in and outside the state of Rio Grande do Sul or, also, provided by other institutions under reciprocal agreements. The healthcare carrier encourages its users to maintain preventive and regular health routines. The employer grants justified absence for the time not worked due to medical appointments, upon submission of a medical certificate, according to a policy on the matter.
Regarding the Covid-19 pandemic, regardless of whether the origin of the contamination is related to the work environment or not, the Bank offers the Telemedicine service in partnership with Hospital Moinhos de Vento, which is available to both Banrisul’s own employees and outsourced workers on permanent contracts. Access is easier with early leave of absence and the use of technology resources that enables a real-time digital doctor’s appointment.
The company offers preventive programs aimed at maintaining overall health, including factors related or not to work. These programs include initiatives aimed at all employees, including:
1) Vacinômetro: campaign to encourage Covid-19 vaccination, according to the Federal Government’s national immunization plan;
2) Annual influenza vaccination campaign: the Bank reimburses the quadrivalent vaccine with coverage for H1N1 and other forms of influenza taken at partner networks;
3) PAD: The Alcohol and Substance Abuse Program offers reimbursement for medical treatment that requires hospitalization for physical and psychological rehabilitation. Costs are paid for even when employees are on social security leave;
4) PASS: an emotional support program for victims of robbery during their work activity, with full reimbursement for the necessary therapies in order to avoid post-traumatic stress disorders. The plan provides membership for 6 months which can be extended for additional 6 months if necessary.
5) PROAT: the program pays for all necessary treatment for the recovery after occupational accidents or illnesses, including doctor’s appointments, medicines, or complementary treatments.
Ratio of basic salary and remuneration of women to men
| Ratio - men/women1 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUPERINTENDENT | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MANAGER | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ANALYST | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ASSISTANT | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ACCESS POSITIONS | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OTHER | 1 | 1 | 1 |
¹There is no difference in the salary of the Bank’s male and female employees, mainly because they are hired through civil service exams.
Banrisul is present in almost 93% of the municipalities. The Bank’s reach comprises service points located both in developed cities with great economic potential and in municipalities that are difficult to access, poorly developed and essentially rural, allowing Banrisul to exceed 99% coverage of the state’s GDP, considering its branches, Service Stations, Banripontos (Banking Correspondents) and Automated Teller Machines (ATMs or PAEs in Portuguese). Banrisul’s presence ensures that the community of the State of Rio Grande do Sul has access to the conveniences offered by the Bank in terms of its financial products and services, which ensure the financing of personal or corporate activities, fostering the State’s economy.
The Bank is continually prospecting cities that lack or have poor offer of banking services. The following table presents the presence of service points throughout the state.
Significant indirect economic impacts
| Presence in Rio Grande do Sul | Number of municipalities | Municipalities coverage | Population coverage | GDP Coverage |
| Branch | 347 | 69.8% | 96.5% | 96.9% |
| Service Station | 81 | 16.3% | 2.1% | 1.9% |
| Subtotal (Branches + Service Stations) | 428 | 86.1% | 98.6% | 98.8% |
| Automated Teller Machines and Banriponto | 6 | 1.2% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Automated Teller Machines | 15 | 3.0% | 0.3% | 0.2% |
| Banriponto | 12 | 2.4% | 0.3% | 0.2% |
| Subtotal (Automated Teller Machines and Banriponto) | 33 | 6.6% | 0.7% | 0.6% |
| Total | 461 | 92.8% | 99.3% | 99.3% |
In 2021, 50 lawsuits with non-monetary sanctions related to social aspects were identified, as provided in CMN Resolution No. 4.557/17, as amended by CMN Resolution No. 4.993/21. These events are identified in the Institution’s Operating Loss Base.
There were no significant fines and lawsuits filed through arbitration mechanisms.
Claims received through specific channels are classified according to the topic, item and root cause. For the matter of the present form, there is the item “banking secrecy,” which belongs to the topic “other topics,” existing for a longer period and the “LGPD” (General Data Protection Act) root cause, created in 2022. In 2021, three customer demands were classified as “banking secrecy”, including external agencies. However, all of them were classified as unfounded, that is, the allegation of data breach was not proven in any of the claims. In addition, no claim was received from a regulatory agency, only from a regulatory entity (Bacen). However, no claim received through this channel in 2021 was related to breach of customer privacy. Furthermore, no leakage, theft or loss of customer data was identified.
100% of Banrisul’s and its affiliates’ contracts with suppliers have specific clauses covering labor and social issues, in accordance with specific legislation.
Through any of its members, the Fiscal Council is responsible for overseeing the Management’s acts and verifying compliance with their legal and statutory duties, according to the Fiscal Council’s Internal Regulation. Some risks are identified, managed and monitored focused on Operational Risk which, consequently, has its control compliance assessed by the Controls and Compliance department.
Even though Banrisul does not have a tax policy approved by the Board or validated by its committees, the Bank adheres to principles to always achieve excellence in adopting good practices to mitigate and reduce tax and fiscal risks. It relies on the internal and external audits as partners in the pursuit of excellence in the management of the institution’s tax matters.
In a broader sense, the responsibilities of the Fiscal and Tax Corporate Department include calculating the institution’s taxes and monitoring all the impacts on the related accessory obligations; supporting the other corporate departments responsible for tax-generating events, whether direct or as tax substitutes, in order to identify possible situations of risk that must be dealt with at the source of the information; in addition to the continuous monitoring of communication with the regulatory and oversight agencies, so as not to generate any burden, whether financial or reputational.
In 2021, Banrisul collected and provisioned R$1,010.9 million in own taxes and contributions. Taxes withheld and passed on, directly levied on financial intermediation and other payments, totaled R$915.2 million in the same period.
The policies or commitments focused on this material topic are the Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Policy (PRSAC, in Portuguese) that regulates processes and business in a comprehensive way; however, the Green Bureau will be soon implemented by the Central Bank (for the Agribusiness segment), which will allow rural credit benefits to be granted to customers who fit the Program’s sustainability criteria.
As regards actions taken to manage this topic and its related impacts, focused on strengthening the offer of rural credit, the Programa Sementes (Seeds Program) and Operation 365 were expanded, which encourage the preservation and maintenance of the chemical, physical and biological quality of the soil, thus increasing productivity. Branch network’s employees receive training, almost every month, on sustainable rural credit products to support the offer of financing for the production of biofertilizers.
In the credit granting process, Banrisul prepares a risk assessment report for transactions totaling more than R$10 million including a social, environmental and climate analysis of the company. To improve and speed up the credit granting process, documents are digitalized and input into a social and environmental compliance system for credit proposals.
The social and environmental compliance system also verifies if the company receiving the financing has any restrictions for the granting of rural credit, e.g., conservation units, IBAMA and ICMBio embargoes, and being listed as a company that use forced labor; therefore, this tool is used to address actual negative impacts arising from this topic. Banrisul also relies on a network of associated technician for preparing projects/budgets.
To track actions taken, the data collected in the system undergo internal and external audits, benchmarking process, and inspections by both the Brazilian Central Bank and the BNDES. Banrisul also hired a consulting company specialized in agribusiness to monitor the internal movements, suggesting process improvements.
These measures aim to comply with the environmental legislations and review the Company’s internal regulations, in order to keep them up to date. Through courses, training programs and verification of the compliance system in all financial departments, Banrisul was able to share and improve the knowledge about social and environmental compliance.
As regards economic impacts, in granting agribusiness credit, the feasibility of the proposals is verified by checking projects and cash flow estimates. To manage positive social impacts, Banrisul does not grant credit to people who have restrictions and makes specific allocations available for small and medium-sized producers. The Bank also offers a crop insurance product called Proagro Mais that covers production costs and funds to maintain the producer’s costs in case of problems with the harvest.
We are always analyzing market trends, proposing projects to develop our reposition products, services, and fees with other product management areas through research, suggestions received through the ombudsman, and benchmarking with the areas. The goal is to increase the granting of rural credit with a sustainable bias.
Focused on creating an investment fund that integrates ESG matters, in 2022, Banrisul held meetings with renowned consulting companies to survey the resources needed to implement this new process. A working group responsible for the “sustainability” topic has been set up in the Company, which has the task of assessing the issue in greater depth and implementing the actions required for the creation/inclusion of ESG investment products in the portfolio.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fostering micro and small entrepreneurs | Positive | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | - | The impact will be generated according to the purpose of the credit granted, usually working capital credit, which will enable the enterprise’s maintenance, as well as small improvements and expansions. | Shareholders and Investors, Community, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Increase family income | Positive | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | - | After credit granting, when the credit facility starts to have financial returns to the creditor. | Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Contamination of soil and bodies of water, and impacts on biodiversity and human health | Negative | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | Medium | Indirectly caused by the granting of credit to rural producers, who use agrochemicals in the soil and generate the impact. | Community, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Increase in renewable energy consumption | Positive | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | - | The rural producer install solar panels or other type of renewable energy source at his/her property, contributing to the increase of clean energy consumption and reduction of conventional energy consumption. | Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Expansion of the agricultural frontier, leading to deforestation or agriculture and livestock activities in forbidden areas | Negative | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | Medium | The rural producer, whether an Individual or Company, who deforests areas without permission to increase the cultivated area, as well as the producer who develops his/her enterprise in a restricted area, such as indigenous lands, Quilombola areas, conservation units, among others. | Community, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Impact on business results for not having ESG-related products in the portfolio yet | Negative | Potential | Short-term | One-time | High | Banrisul Corretora de Valores is aware that it may lose customers for not having ESG-related products in its portfolio yet, as investors, especially younger generations, seek to relate to sustainable or purpose-driven companies. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Community, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
*Values in thousands of Reais
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added value for distribution | 3,830,545 | 3,856,741 | 3,534,307 | |||
| Net Revenue | 3,830,545 | 100% | 3,856,741 | 100% | 3,534,307 | 100% |
| Economic value distributed | 3,321,033 | 86.7% | 3,290,155 | 85.3% | 3,179,300 | 90.0% |
| Personnel (salaries and benefits) | 1,992,630 | 59.2% | 1,767,289 | 52.5% | 2,033,022 | 57.5% |
| Taxes, Fees and Contributions | 989,855 | 29.4% | 1,010,938 | 30.1% | 649,833 | 18.4% |
| Third-party capital | 120,382 | 3.6% | 129,709 | 3.9% | 136,099 | 3.9% |
| Interest on equity and dividends | 218,166 | 6.5% | 382,219 | 11.4% | 360,346 | 10.2% |
| Retained economic value | 509,512 | 13.3% | 566,586 | 14.7% | 355,007 | 10.0% |
| Product name | Monetary value | % of Banrisul Credit Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Agribusiness Credit Facilities | 5.5% | |
| ABC+ Program | R$28,582,438.7 | 0.1% |
| Pronaf (Brazilian National Program for Strengthening Family Farming) ABC+ Bioeconomia | R$23,331,764.0 | 0.0% |
| Pronaf (Brazilian National Program for Strengthening Family Farming) Mais Alimentos | R$208,166,706.2 | 0.4% |
| Pronaf (Brazilian National Program for Strengthening Family Farming) Agroindústria | R$5,509,827.3 | 0.0% |
| Pronamp (National Program for the Support of Medium-Sized Farmers) | R$29,185,719.7 | 0.1% |
| Moderagro | R$41,819,775.9 | 0.1% |
| Inovagro | R$9,695,855.5 | 0.0% |
| Proirriga | R$69,708,249.4 | 0.1% |
| PCA | R$26,877,667.1 | 0.1% |
| Investimento Agro Empresarial (Corporate Investment in Agriculture) | R$64,863,709.4 | 0.1% |
| Agroinvest 4.0 - New technologies | R$1,065,246.0 | 0.0% |
| Agroinvest Sustainability | R$29,502,272.4 | 01% |
| Funding for no-till farming | R$ 2,151,555,320.7 | 4.4% |
| Commercial Credit Facilities | 2.0% | |
| CDC Universitário (Direct Consumer Credit Facility for University Students) | R$68,006,326.0 | 0.1% |
| CDC Sustentabilidade Outros PF e PJ (Other Sustainable Direct Consumer Credit Facility for Individual and Corporate Customers) | R$3,170,021.0 | 0.0% |
| CDC Sustentabilidade Energias Solar e Eólica PF e PJ (Sustainable Direct Consumer Credit Facility - Solar and Wind Power for Individual and Corporate Customers) | R$ 565,902,465.1 | 1.2% |
| CPB Acessibilidade (Accessiblity) | R$10,164.4 | 0.0% |
| CEB Hospitais - Giro - Investimento (Banrisul Corporate Credit - Hospital's Working Capital) | R$206,865,259.0 | 0.4% |
| CPB Crédito Consciente (Conscious Credit) | R$141,248,746.4 | 0.3% |
| CPB Emergencial (Emergency Credit) | R$93,757.1 | 0.0% |
| Long-Term Financing | 2.5% | |
| FEB – Financiamento Especial Banrisul (Banrisul Special Financing) | R$ 88,205,698.4 | 0.2% |
| PRONAMPE - National Program of Support to Micro and Small Companies | R$ 1,032,711,573.7 | 2.1% |
| Programa Saneamento Para Todos (Sanitation for Everyone Program) | R$ 30,324,429.6 | 0.1% |
| Banrisul FAMPE Mais - Individual Micro Entrepreneur (ME) and Micro e Small Company | R$ 79,339,259.0 | 0.2% |
| Fundo Clima | R$ 15,425,769.8 | 0.0% |
| Credit Cards | Monetary Value | Customers |
| Cartão Libre | R$ 1,259.4 milhões | 265,099 |
| Cartão Universitário (Credit Card for University Students) | R$ 314 milhões | 34,467 |
| Cartão Servidor Público (Card for Public Servants) | R$ 1,109.05 milhões | 79,502 |
| INSS Payroll-Deductible Card | R$ 248.5 milihões | 173,365 |
| Product/service description | Purpose | Target social group |
|---|---|---|
| Agribusiness Credit Facilities | ||
| ABC+ Program | Credit facility to promote a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, reduce deforestation, increase agriculture and livestock production on a sustainable basis, adapt rural properties to the environmental legislation, expand the area of cultivated forests, encourage the recovery of degraded areas. | Family farms who are registered in the Pronaf. |
| Pronaf (Brazilian National Program for Strengthening Family Farming) ABC+ Bioeconomia | Credit facility for investments in Extractive Exploration, Socio-Biodiversity Products Systems, Renewable Energy and Environmental Sustainability. | Medium-sized or large rural producers and their production cooperatives. |
| Pronaf (Brazilian National Program for Strengthening Family Farming) Mais Alimentos | Credit Faciliy for investments in income generation and improvement of manpower in family farms. Sustainable items include technological innovation in renewable energy, e.g., solar power, biomass and windpwer. | Family farms who are registered in the Pronaf. |
| Pronaf (Brazilian National Program for Strengthening Family Farming) Agroindústria | Credit facility to investments, including in infrastructure, aimed at the improvement, storage, processing and trade of agriculture and livestock products, forest and extractivist products, handicraft products and rural tourism. | Family farms who are registered in the Pronaf, their family enterprises and family agriculture cooperatives. |
| Pronamp (National Program for the Support of Medium-Sized Farmers) | Credit facility to foster the development of medium-sized farmers’ rural productive activities, through credit for fixed and partially fixed investments in agriculture-related assets and services. Finance includes soil protection, correction, and recovery; renewable energy generation systems; and organic systems. | Medium-sized farmers registered in the Pronamp. |
| Moderagro | Credit facility to support the production, processing, industrialization, packaging and storage of products from beekeeping, aquaculture, poultry farming, chinchilla farming, rabbit farming, flower farming, fruit farming, olive growing, horticulture, sheep and goat farming, ranching, sericulture, pig farming, dairy farming and palm farming, yerba mate, nuts, fishing and sugar cane for the production of cachaça. Finances some items such as the execution of a sanitary and/or environmental adequacy project, related to the business line's purpose. | Medium-sized or large rural producers and their production cooperatives |
| Inovagro | Credit facility to support the necessary investments to incorporate technological innovation into rural properties in order to increase productivity, the adoption of good agriculture, livestock and farm management practices, and the competitive insertion of rural producers in different consumer markets. Finances items such as renewable energy generation and distribution systems (solar and biomass). | Medium-sized or large rural producers and their production cooperatives. |
| Proirriga | Credit faclity for finance investments in all items related to irrigation systems, including electrical infrastructure, water reserve, and equipment for monitoring soil humidity; the acquisition, implementation, and recovery of equipment and facilities for crop protection inherent to olericulture, fruit-growing, flower-growing, coffee-growing, and the production of seedlings of forest species; and the meteorological stations and software necessary for their operation. | Medium-sized or large rural producers and their production cooperatives. |
| PCA | Credit facility for projects for the expansion, modernization, renovation, and construction of warehouses to store grains, fruits, tubers, bulbs, vegetables, fibers, and sugar. | Medium-sized or large rural producers and their production cooperatives. |
| Investimento Agro Empresarial (Corporate Investment in Agriculture) | To finance the same purposes met by Programs that use BNDES resources, it is possible to list some sustainability-related items, such as: environmental regularization of rural property, forestation and reforestation, and acquisition of solar panels. | Rural producers that meet corporate agriculture requirements. |
| Agroinvest 4.0 - New technologies | To finance drones, sensors, mapping software licenses, Global Positioning System (GPS), precision agriculture equipment; as well as computers, equipment and software licenses for property management, monitoring or automation. Fostering the modernization of the countryside and the improvement in the producers’ quality of life. | Individual farmers, registered in any category, with risk up to 6. |
| Agroinvest Sustainability | Line of credit for financing solar energy conversion systems and panels, as well as biodigesters. Line with 100% sustainable bias. | Individual farmers, registered in any category, with risk up to 6. |
| Funding for no-till farming | Credit Facility for the regular expenses of farms that use no-till farming. | Rural producers |
| Commercial Credit Facilities | ||
| CDC Universitário (Direct Consumer Credit Facility for University Students) | Credit facility developed to finance all higher education programs and types (on-campus and hybrid) of the partner universities. Banrisul has partnered with 13 universities: FACCAT, FEEVALE, IMED, PUCRS, UNISINOS, URI, UNISC, UNIJUI, UNIVATES, URCAMP, UCS, UCPEL and UPF, for students in Rio Grande do Sul. | Undergraduate students. |
| CDC Sustentabilidade Outros PF e PJ (Other Sustainable Direct Consumer Credit Facility for Individual and Corporate Customers) | To finance the acquisition of products to preserve energy resources, reuse water, and promote sustainable urban mobility. | Individual and Corporate Customers. |
| CDC Sustentabilidade Energias Solar e Eólica PF e PJ (Sustainable Direct Consumer Credit Facility - Solar and Wind Power for Individual and Corporate Customers) | To finance the acquisition of solar panels and wind power turbines, focused on clean energy generation | Individual and Corporate Customers. |
| CPB Acessibilidade (Accessibility) | Finance the acquisition of goods and services for people with disabilities. | People with disabilities. |
| CEB Hospitais - Giro - Investimento (Banrisul Corporate Credit - Hospital's Working Capital) | Credit facility to offer Working Capital and Investment to non-profit private hospitals, clinics and laboratories in Rio Grande do Sul, which provide services to the Brazilian Public Health System (called SUS) and receive payments from SUS and other public or private health care plans. | Entire community served by the hospitals. |
| CPB Crédito Consciente (Conscious Credit) | Credit facility aimed at renegotiating overdue debts, preventing the customer’s over-indebtedness. | It is targeted at individuals with indebtedness up to 60 days. |
| CPB Emergencial (Emergency Credit) | Credit facility granted on an emergency basis exclusively to individuals, residents in municipalities whose houses have been affected by natural disasters (windstorms, floods, rain, etc.), provided that the Office of Civil Defense has declared a state of emergency. | It is aimed at individuals who have been affected by state of emergency. |
| Long-Term Financing | ||
| FEB – Financiamento Especial Banrisul (Banrisul Special Financing) | Credit facility targeted at the Municipalities of the State of Rio Grande do Sul that are qualified to contract new financings according to the legislation that provides for the indebtedness limit for the Public Sector. This facility can be used to finance capital goods, such as renewable energy generating systems, computer systems/software and hardware, buses, trucks, vehicles, new machinery and equipment, produced domestically or that have already been nationalized and preferably those listed in the BNDES’s Digital Record of Manufacturers (CFI, in Portuguese). The municipality’s current expenses (e.g., payroll expenses, expenses with the maintenance of fixed assets, office suppliers and consumables) cannot be financed. | Municipalities in the State of Rio Grande do Sul. |
| PRONAMPE - National Program of Support to Micro and Small Companies | Credit facility granted within the scope of the National Program of Support to Micro and Small Companies (PRONAMPE, in Portuguese), initially regulated by Law 13.999/2020, amended by Law 14.161/2021, and guaranteed by the Operations Guarantee Fund (FGO, in Portuguese) for the development and strengthening of small businesses. It is aimed at individual micro-entrepreneurs (MEI, in Portuguese) and companies with gross revenue equal to or less than R$ 4.800.000,00 (four million and eight hundred thousand Brazilian Reais), considering the income earned in the fiscal year immediately previous to that of the credit granting. | Micro and small companies. |
| Programa Saneamento Para Todos (Sanitation for Everyone Program) | Credit facility designed to improve health conditions and quality of life of the urban and rural population through investments in sanitation integrated and articulated with other sector policies, operating based on systems run by public or private providers, through initiatives and undertakings targeted at the universal access to sanitation and improvement of the public basic sanitation services, according to normative instruments that govern investment programs and portfolios managed by the FGTS, as determined by the investment manager. The projects must adopt technical solutions that seek economic efficiency gains and management solutions that promote efficient services and incorporate social control and the participation of society. | Municipalities in the State of Rio Grande do Sul. |
| Banrisul FAMPE Mais - Individual Micro Entrepreneur (ME) and Micro e Small Company | Credit facility designed to finance working capital for individual micro-entrepreneurs (MEI) and micro and small business that relies on the Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (FAMPE), replacing the need for guarantee from the Bank, providing entrepreneurs with easier access to credit. This line has Assisted Credit, made available in partnership with Sebrae RS, with free-of-charge content available to all customers and consulting services on specific topics, also made available free of charge to borrowers, and fully funded by Banrisul and Sebrae RS. | It is targeted at individual micro-entrepreneurs (MEI) and micro and small businesses. |
| Fundo Clima | Credit facility designed to finance the acquisition of machinery and equipment with higher energy efficiency indexes or that contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, such as solar panels. | It is aimed at individuals or corporate customers with annual income or revenue of up to R$4.8 million. |
| Credits Cards | ||
| Every month, the credit card bill is rounded up to the next whole number and the cents are donated to charity institutions. | To make contributions to charity institutions through the donation of amounts collected in the Card Bill Rounding Up Program. | Charity Institutions. |
| Issue of credit card for enrolled university students, who do not need to prove their income, thus encouraging their higher education studies as well as financial education. | To introduce college customers to banking services and foster their financial education through the use of credit cards. | University students with or without income |
| A distinguished credit card that offers reduced interest rates, longer payment terms, and discount on the minimum payment directly on the payroll. | To provide a social benefit to public servants, enabling a distinguished experience with reduced interest rates, longer payment terms, and discounts on the payroll. | Public Servants. |
| Credit card aimed at retirees and pensioners, allowing to deduct 5% of their monthly income in the INSS payroll, previously authorized through an amendment at DATAPREV. | To provide social benefits to retirees and pensioners, according to the legislation, allowing to deduct 5% of their monthly income. | INSS retirees and pensioners. |
Banrisul is concerned about the credibility of its information disclosed to the market and submits its sustainability report to independent external limited assurance by Deloitte, which also audits the financial statements.
The assurance letter can be found in the Sustainability Report on page 119.
| Waste generated by type and disposal (t) | ||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ∆2021/2020 | |
| Non-hazardous waste - Class II¹ | ||||
| Safes - Recycling and donation | 5.8 | 0.0 | 10.4 | - |
| Metal (scraps) - Recycling | 179.1 | 45.4 | 114.1 | 151.5% |
| Banners, shredded cards and acrylic - Recycling | 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.8 | - |
| Paper - Recycling | 211.22 | 128.5 | 206.6 | 60.8% |
| Electronics - Recycling | 50.3 | 49.7 | 93.4 | 87.8% |
| Co-processing | 26.6 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 427.6% |
| Total waste generated | ||||
| Total waste diverted from disposal - Non-hazardous | 446.6 | 223.6 | 427.3 | 91.1% |
| Total waste directed to disposal - Non-hazardous | 26.6 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 427.6% |
| Overall total | 473.2 | 223.9 | 428.8 | 91.6% |
| ¹As for the organic waste generated in the organization, these are destined for public collection in the locations where agencies and units are located. In the administrative headquarters building there is a company hired to dispose of organic waste. There is no mapping of the amount of organic waste generated. | ||||
| Waste generated by type and disposal (unit) | ||||
| Hazardous waste - Class I | ||||
| Lamps - Recycling | 5,713.0 | 1,652.0 | 2,060.0 | 24.7% |
| Total waste diverted from disposal - Hazardous | 5,713.0 | 1,652.0 | 2,060.0 | 24.7% |
| Non-hazardous waste - Class II | ||||
| Donation of furniture - Reuse | 5,724.0 | 2,127.0 | 4,999.0 | 135.0% |
| Total waste diverted from disposal - Non-hazardous | 5,724.0 | 2,127.0 | 4,999.0 | 135.0% |
| Total waste generated | ||||
| Total waste diverted from disposal | 11,437.0 | 3,779.0 | 7,059.0 | 86.8% |
| Overall total | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | - |
Banrisul’s strategy is aims to set up partnerships to increase the number of microcredit operations. For the year 2022, the Bank plans to make progress in the partnership with the union of motorcycle couriers, offering microcredit lines at special conditions for the acquisition of new motorcycles, safety equipment for use in the activity of motorcycle couriers, and the financing of bicycles, contributing to the safe delivery of orders.
As regards loans to promote small businesses and community development, three credit operations were granted, totaling R$ 13,600.00 in 2021.
No data breach was identified in the reporting period.
Credit operations for small enterprises and community development are listed in the table for indicator FS7.
Total number and percentage of total points of access available in low-populated or economically disadvantaged areas by region and by type of access
| Below Urbanization Rate | Quantility |
| Number of municipalities | 404 |
| With Banking Services | 368 |
| Coverage | 91.09% |
| Number of Points | 941 |
In order to identify Banrisul’s presence in low-populated or economically disadvantaged areas, the Bank uses the urbanization rate criterion, covering only the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The average parameter was 85.1%, establishing 404 locations with a lower indicator. Out of this total, 91% (368) have some type of banking service. The number of points in these municipalities totals 941, including branches, banking stations, Automated Teller Machines and Banripontos.
Performance evaluation is an essential step to assess effectiveness, contributing to enhance the Organization’s governance. The Board of Directors carries out an annual formal evaluation of the Executive Board and its Chair performance, as well as of its own performance, a process that include self-evaluation questions. The annual evaluation is carried out according to procedures previously defined by the Board of Directors and is anonymous and individual.
All answers to the evaluation questionnaires are compiled into a report, which is sent to the Eligibility and Compensation Committee for prior analysis and then presented to the Board of Directors for consideration. The body itself suggests improvements in carrying out their duties.
Banrisul’s organizational structure includes the Internal Audit department, reporting to the Board of Directors, whose scope of activities considers all duties of Banrisul and the other companies in the conglomerate, in compliance with CMN Resolution 4,879/2020.
Therefore, as of the publication of CMN Resolution 4,945, of September 15, 2021, an audit forecast was included in the Internal Audit planning for 2022. Works began in August 2022 and were completed in February 2023. For 2023, a social, an environmental and climate risk management audit is planned according to CMN Resolution 4,557, of February 23, 2017.
The internal audit department is responsible both for the past and for the future audit, as per:
– CMN Resolution 4,945, of September 15, 2021
– CMN Resolution 4,557, of September 23, 2017
Below, we list some Internal Audit findings that are currently being monitored. We must note that all the findings/reports issued by the Internal Audit are in compliance with the Policy on Management of Internal Audit Findings, approved by the Conglomerate’s Board of Directors:
– Actions to ensure PRSAC’s Effectiveness: drafting/preparation and validation of indicators relates to the Sustainability Agenda. Expectation to hire an external consulting firm to assist in this process. Timetable/deadlines will be established by the managing department.
– Dissemination of Complete and Updated Information: combined actions of the Sustainability Corporate Department and the Institution’s other departments, in addition to the creation of working groups for mapping sustainable products and sensitive sectors as regards social, environmental or climate aspects, as well as the forecast for hiring external consultants to assist in this project. Timetable/deadlines will be established by the managing department.
– Implementation of the PRSAC: initiatives to enable the implementation of social, environmental and climate responsibility principle and guidelines established in the PRSAC, as well as to ensure their compatibility and integration with the Institution’s other policies. Expectation to hire an external consulting firm to assist in this process. Timetable/deadlines will be established by the managing department.
The institution has seven officers, one CEO and nine directors, totaling 17 members, and all of them have been informed about anti-corruption policies. Moreover, 9,002 employees have been informed about said practices, accounting for 100% of the staff. The updated policy has been informed through Normative Instruction and made available through a Distance Learning training.
Banrisul has been working constantly with Bem Promotora on the Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing (PLDFT in Portuguese).
The Anti-Corruption policy aims to give visibility and to lay down the ethical principles and values that should guide the actions of employees, service providers, correspondents and all third parties who perform any activity on behalf or in interest of Banrisul. The policy is published on the Intranet Portal and the Investor Relations website;Two members of governance bodies received anti-corruption training, both from Porto Alegre, acting in committees and heading the Controls, Compliance and Financial Controller Units.
Total number of employees that have received training on anti-corruption, broken down by employee category
| Total number of employees that have received training on anti-corruption, broken down by employee category | |
|---|---|
| Employee category | Quantity |
| Analyst | 304 |
| Consulting Advisor | 2 |
| Legal Advisor | 2 |
| Assistant | 8 |
| Auditor | 28 |
| Cashier | 29 |
| Head of audit department | 3 |
| Corporate Manager | 1 |
| Associate Manager | 27 |
| Commercial manager | 2 |
| Agribusiness manager | 1 |
| Foreign exchange manager | 2 |
| Account manager | 5 |
| Market manager | 10 |
| Business manager | 27 |
| Collection team manager | 2 |
| Executive manager | 36 |
| General manager | 18 |
| Agribusiness relationship manager | 2 |
| Business operator | 33 |
| Employees trained on the Bank’s cybersecurity platform | 188 |
| Without position | 69 |
| Executive superintendent | 5 |
| Supervisor | 11 |
| Occupational safety technician | 1 |
| Total | 816 |
Total number of employees that have received training on anti-corruption, broken down by region
| Total number of employees that have received training on anti-corruption, broken down by region | |
|---|---|
| Digital branch | Quantity |
| General management - Administrative departments | 1 |
| Downtown superintendency | 398 |
| Boarder superintendency | 32 |
| East superintendency | 33 |
| Northwest superintendency | 61 |
| “Serra” superintendency | 33 |
| South superintendency | 64 |
| Alto Uruguay Superintendency | 27 |
| Sureg other states | 43 |
| Porto Alegre downtown Sureg | 30 |
| Porto Alegre Sureg | 28 |
| Total | 66 |
| 816 | |
In the period, no analyzed nor confirmed incidents of corruption were identified. Moreover, the Bank does not have information on agreements that have been terminated or not renewed due to involvement or possible involvement of a correspondent with corruption. In 2021, only one process was registered, related to fraud in a contract by an employee, but it is still in progress and, therefore, there was no penalty or termination.
| Energy consumption within the Organization (GJ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | ∆2021/2022 | |
| Non-renewable fuels (diesel) | 94.8 | 270.2 | 218.1 | -19.3% |
| Electricity purchased from the concessionaire1 | 120,590.6 | 132,062.5 | 122,276.3 | -7.4% |
| Total energy consumption | 120,685.4 | 132,332.7 | 122,494.4 | -7.4% |
¹In 2020, as it was the first inventory carried out by the institution, only Banrisul’s energy consumption was verified, without considering the other companies in the group (Bagergs and Banrisul Pagamentos), which was measured from the following inventories.
Banrisul’s organizational structure includes the Internal Audit department, subordinated to the Board of Directors, whose scope of activities considers all duties of Banrisul and the other companies in the conglomerate, in compliance with CMN Resolution 4,879/2020. Therefore, as of the publication of CMN Resolution No. 4,945, of September 15, 2021, an audit forecast was included in the Internal Audit planning for 2022.
Banco do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (Banrisul) is a government-controlled corporation. Banrisul’s General Management, its administrative headquarters, is located in the city of Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul state.
Banrisul’s Whistleblowing Channel is a communication tool through which employees, customers, users, partners or suppliers report possible misconducts of any nature related to the Institution’s activities that affect its reputation and violate its internal controls and Banrisul’s Compliance Program. The whistleblowing channel is available on the Bank’s institutional website or on the intranet, where a registration form can be filled out anonymously.
The internal and external channels for submitting complaints and queries covered by the Policy are disclosed, respectively, on the Corporate Intranet and on Banrisul’s website – www.banrisul.com.br, in the section Whistleblowing Channel.
In the event of non-compliance with this Policy and related regulations, actions will be taken according to the level of the offender’s relationship with the Bank:
– if an Employee, sanctions provided for in item Sanctions of the Personnel Regulations will be adopted, appropriate to address the non-compliance;
– if an Officer or Board/Committee Member, the non-compliance will be reported by the Internal Audit to the Board of Directors, complying, when applicable, to Banrisul’s Whistleblowing Policy;
– if an Intern or Outsourced Employee, sanctions provided for in the agreement will be adopted.
If managers, other employees and/or other related parties become aware of misconducts and do not report them to the Personnel Department or the Whistleblowing Channel, they will also be held accountable.
Regardless of the degree of relationship with Banrisul and the penalty adopted, anyone who fails to comply with the organizational policies may be held civilly or criminally liable for proven misconduct.
Direct economic value generated and distributed (R$ thousand)
| Direct economic value generated and distributed (R$ thousand) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||
| Added value for distribution | 4,171,826 | 100% | 3,830,545 | 100% | 3,856,741 | 100% |
| Net Revenue | 4,171,826 | 100% | 3,830,545 | 100% | 3,856,741 | 100% |
| Economic value distributed | 3,363,518 | 80.6% | 3,321,033 | 86.7% | 3,290,155 | 85.3% |
| Personnel (salaries and benefits) | 1,839,392 | 54.7% | 1,992,630 | 59.2% | 1,767,289 | 52.5% |
| Taxes, Fees and Contributions | 872,044 | 25.9% | 989,855 | 29.4% | 1,010,938 | 30.1% |
| Remuneration on Third-Party Capital | 115,451 | 3.4% | 120,382 | 3.6% | 129,709 | 3.9% |
| Interest on equity and dividends | 536,631 | 16.0% | 218,166 | 6.5% | 382,219 | 11.4% |
| Retained economic value | 808,308 | 19.4% | 509,512 | 13.3% | 566,586 | 14.7% |
Percentage of individuals whitin the organization's governance bodies in each of the following diversity categories
| Percentage of individuals within the organization’s governance bodies in each of the following diversity categories: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I) Gender | ||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||
| Gender | Total | % | Total | % | Total | % |
| Men | 34 | 85.0% | 34 | 85.0% | 36 | 90.0% |
| Women | 6 | 15.0% | 6 | 15.0% | 4 | 10.0% |
| Total | 40 | 100% | 40 | 100% | 40 | 100% |
Percentage of individuals whitin the organization's governance bodies in each of the following diversity categories
| Percentage of individuals within the organization’s governance bodies in each of the following diversity categories: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II) Age group: under 30 years old, 30-50 years old, over 50 years old | ||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||
| Age group | Total | % | Total | % | Total | % |
| Under 30 years old | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% |
| 30-50 years old | 15 | 37.5% | 13 | 32.5% | 11 | 27.5% |
| Over 50 years old | 25 | 62.5% | 27 | 67.5% | 29 | 72.5% |
| Total | 40 | 100% | 40 | 100% | 40 | 100% |
Percentage of individuals whitin the organization's governance bodies in each of the following diversity categories
| Percentage of employees per employee category in each of the following diversity categories: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I) Gender | |||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||
| Employee category | Gender | Total | % | Total | % | Total | % |
| Superintendent | Men | 49 | 72.1% | 47 | 70.2% | 45 | 66.2% |
| Women | 19 | 27.9% | 20 | 29.8% | 23 | 33.8% | |
| Total | 68 | 100% | 67 | 100% | 68 | 100% | |
| Manager | Men | 1,036 | 62.0% | 980 | 61.8% | 985 | 61.1% |
| Women | 636 | 38.0% | 607 | 38.3% | 627 | 38.9% | |
| Total | 1,672 | 100% | 1,587 | 100% | 1,612 | 100% | |
| Analyst | Men | 917 | 64.3% | 926 | 62.7% | 1,093 | 61.4% |
| Women | 508 | 35.6% | 550 | 37.3% | 686 | 38.6% | |
| Total | 1,425 | 100% | 1,476 | 100% | 1,779 | 100% | |
| Assistant | Men | 227 | 49.5% | 170 | 55.9% | 94 | 63.5% |
| Women | 232 | 50.5% | 134 | 44.1% | 54 | 36.5% | |
| Total | 459 | 100% | 304 | 100% | 148 | 100% | |
| Without commissioned position | Men | 3,108 | 50.4% | 2,760 | 51.2% | 2,503 | 50.2% |
| Women | 3,056 | 49.6% | 2,628 | 48.8% | 2,486 | 49.8% | |
| Total | 6,164 | 100% | 5,388 | 100% | 4,989 | 100% | |
| Other | Men | 279 | 56.4% | 246 | 53.7% | 226 | 55.7% |
| Women | 216 | 43.6% | 212 | 46.3% | 180 | 44.3% | |
| Total | 495 | 100% | 458 | 100% | 406 | 100% | |
| Total | Men | 5,616 | 54.6% | 5,129 | 55.3% | 4,946 | 54.9% |
| Women | 4,667 | 45.4% | 4,151 | 44.7% | 4,056 | 45.1% | |
| Overall total | 10,283 | 100% | 9,280 | 100% | 9,002 | 100% | |
Percentage of individuals whitin the organization's governance bodies in each of the following diversity categories
| Percentage of employees per employee category in each of the following diversity categories: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II) Age group: under 30 years old, 30-50 years old, over 50 years old | |||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||
| Employee category | Age group | Total | % | Total | % | Total | % |
| Superintendent | Under 30 years old | - | 0.0% | - | 0.0% | - | 0.0% |
| 30-50 years old | 26 | 38.2% | 25 | 37.3% | 22 | 32.4% | |
| Over 50 years old | 42 | 61.8% | 42 | 62.7% | 46 | 67.6% | |
| Total | 68 | 100% | 67 | 100% | 68 | 100% | |
| Manager | Under 30 years old | 48 | 2.9% | 31 | 2.0% | 25 | 1.6% |
| 30-50 years old | 1,050 | 62.8% | 1,082 | 68.2% | 1,112 | 69.0% | |
| Over 50 years old | 574 | 34.3% | 474 | 29.9% | 475 | 29.5% | |
| Total | 1,672 | 100% | 1,587 | 100% | 1,612 | 100% | |
| Analyst | Under 30 years old | 16 | 1.1% | 30 | 2.0% | 36 | 2.0% |
| From 30 to 50 years old | 858 | 60.2% | 911 | 61.7% | 1,161 | 65.3% | |
| Over 50 years old | 551 | 38.7% | 535 | 36.2% | 582 | 32.7% | |
| Total | 1,425 | 100% | 1,476 | 100% | 1,779 | 100% | |
| Assistant | Under 30 years old | 33 | 7.2% | 22 | 7.2% | 3 | 2.0% |
| From 30 to 50 years old | 340 | 74.1% | 212 | 69.7% | 102 | 68.9% | |
| Over 50 years old | 86 | 18.7% | 70 | 23.0% | 43 | 29.1% | |
| Total | 459 | 100% | 304 | 100% | 148 | 100% | |
| Without commissioned position | Under 30 years old | 594 | 9.6% | 393 | 7.3% | 211 | 4.2% |
| From 30 to 50 years old | 3,779 | 61.3% | 3,659 | 67.9% | 3,416 | 68.5% | |
| Over 50 years old | 1,791 | 29.1% | 1,336 | 24.8% | 1,362 | 27.3% | |
| Total | 6,164 | 100% | 5,388 | 100% | 4,989 | 100% | |
| Other | Under 30 years old | 17 | 3.4% | 8 | 1.7% | 2 | 0.5% |
| From 30 to 50 years old | 265 | 53.5% | 274 | 59.8% | 232 | 57.1% | |
| Over 50 years old | 213 | 43.0% | 176 | 38.4% | 172 | 42.4% | |
| Total | 495 | 100% | 458 | 100% | 406 | 100% | |
| Total | Under 30 years old | 708 | 6.9% | 484 | 5.2% | 277 | 3.1% |
| From 30 to 50 years old | 6,318 | 61.4% | 6,163 | 66.4% | 6,045 | 67.2% | |
| Over 50 years old | 3,257 | 31.7% | 2,633 | 28.4% | 2,680 | 29.8% | |
| Overall total | 10,283 | 100% | 9,280 | 100% | 9,002 | 100% | |
The Board of Directors (BoD) is responsible for acting on behalf of the Institution in the Risk Appetite Statement (RAS) supported by the Risk Committee (RC), the Executive Board and the CRO. The Disclosure Policy is considered in assessing RWA amount and adequacy to PR. The Board of Directors mainly focuses on the review and approval of:
- Capital management policies, strategies and limits;
- Stress Testing Program;
- Policies for Business Continuity Management;
- Liquidity Contingency Plan;
- Internal Simplified Assessment Process for Capital Adequacy (ICAAPSIMP) and Capital Plan; and
- Capital Contingency Plan.
The Board of Directors (BoD) ensures that the institution complies with the policies, strategies and its own limits, considering possible timely corrections to structural deficiencies. Its responsibilities also include the capacity to approve significant changes to policies and strategies as well as systems, routines and procedures, such as:
- Products and services;
- Hedging strategies and risk-taking initiatives;
- Significant corporate reorganizations; and
- Changes to the macroeconomic outlook.
Another responsibility of the Board is the capacity to ensure the appropriate and sufficient culture and resources to carry out the activities in an independent, objective and effective manner, based on the legislation in force. It is necessary to approve the appointment and removal of the officer in charge and the organizational structure for capital and corporate risk management.
Total direct and indirect (Scope 1, 2 and 3) GHG emissions in metric tonnes of CO2 equivalent
Emissions
| Type of emission | 2020 Amount (in TCO2e)² | 2021 Amount (in TCO2e) |
| Total direct emissions (Scope 1) | 639.7 | 958.9 |
| Total indirect emissions (Scope 2) | 2,067.6 | 4,642.3 |
| Total other indirect emissions (Scope 3) | 31.0 | 5,054.4 |
| Biogenic emissions of CO2 | 6.9 | 871.9 |
| Other - HCFC 22 (R22) | 2,970.7 | 3,010.0 |
| Total¹ | 5,716.0 | 14,537.5 |
¹From the reference year 2020 to 2021, emissions from energy consumption increased mainly due to the growth in the emission factor, arising from the water crisis and the need to use energy from sources that contribute to Greenhouse Gas emissions. In 2021, the group’s companies were also included in the GHG Inventory, leading to an increase in emissions due to an improvement in data gathering.
²2020 was the year in which Banrisul prepared its first GHG inventory, using this year as the basis for its future inventories.
For purposes of calculating scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions, all gases (CO2, CH4, N2O, HFCs, PFCs, SF6, NF3) were considered, according to the methodology adopted by the Brazil GHG Protocol Program.
In the second GHG inventory, prepared in 2021, the Bank included rented cars in scope 1 emissions, as well as an analysis of electricity consumption at some leased venues in scope 2. In 2020, scope 3 included only business air travel, and for 2021, emissions related to transport and distribution (Upstream), business air and land travel, and employee commuting (home – work) were added.
Since the preparation of the first inventory in 2020, Banrisul has planned advancements and improvements in data gathering and in projects to mitigate emissions. For the upcoming cycle, the Institution plans to begin calculating emissions in the credit portfolio and in some other scope 3 categories, such as waste generation. In addition to officially disclosing the goal of reducing emissions by 2030, the Bank plans to adhere to some framework for managing its emissions.
The Renewable Energy Project is progress with the goal of migrating Banrisul’s energy consumption matrix to renewable sources, expected to start in 2022 and gradually transition the Bank’s branches and administrative buildings.
Employees, by gender¹ ²
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total | |
| Permanent and full-time employees | 5,129 | 4,151 | 9,280 | 4,946 | 4,056 | 9,002 | 4,729 | 3,929 | 8,658 |
¹Banrisul does not have temporary, non-guaranteed hours and part-time employees.
²All permanent employees are full-time employees.
Employees, by region
| Region¹ | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Midwest | 9 | 7 | 8 |
| South | 9,214 | 8,939 | 8,600 |
| Southeast | 57 | 56 | 50 |
| Total | 9,280 | 9,002 | 8,658 |
¹Banrisul does not have employees in the North and Northeast regions.
Data were gathered from a proprietary system, considering total employees for the reference period.
Energy consumption within the organization(GJ)²
| 2020 | 2021 | ∆2021/2020¹ | |
| Non-renewable fuels consumption | |||
| Diesel | 94.8 | 270.2 | 185.1% |
| Electricity consumption | |||
| Electricity from concessionary | 120.6 | 132.1 | 9.5% |
| Total energy consumption | 215.4 | 402.3 | 86.8% |
¹There was an increase in diesel consumption due to the instabilities in energy supply from the distribution network. Additionally, the collection process gathered data that had not been accounted for in the previous cycle, such as energy consumption in leased venues.
²In the Inventory of GHG emissions, an additional 20 liters of diesel oil and 38,545 kWh of electricity consumed were reported, and the values presented in the table, for the year 2021, have been corrected.
Note: Only the Brazil GHG Protocol Program methodology was used.
Source for data conversion factors: 2021 National energy balance (reference year 2020). Available at: https://www.epe.gov.br/sites-pt/publicacoes-dados-abertos/publicacoes/PublicacoesArquivos/publicacao-601/topico-596/BEN2021.pdf
The consolidated financial statements include the operations of Banrisul, its offices abroad, its subsidiaries (Banrisul Armazéns Gerais S.A., Banrisul S.A. Corretora de Valores Mobiliários e Câmbio, Banrisul S.A. Administradora de Consórcios, Banrisul Soluções em Pagamentos S.A., Banrisul Seguridade Participações S.A.) and investment fund quotas in which Banrisul substantially takes or incurs in risks and benefits. We explain the Banrisul Group in detail, which comprises six subsidiaries and four affiliated companies.
In 2021, an act of infringement (of non-monetary sanction) and a new lawsuit in progress, with no recorded losses, were identified. The information regarding the content of the events and amounts is considered strategic for the management processes. Furthermore, there were no significant fines and lawsuits filed through arbitration mechanisms.
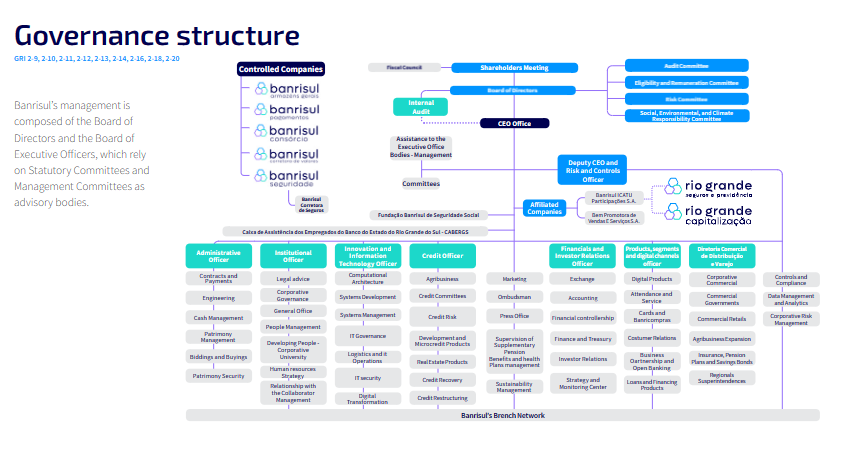
BOARD OF DIRECTORS
| Name | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jorge Luís Tonetto | Chairman - non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Claudio Coutinho Mendes | Vice chairman - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Irany de Oliveira Sant’Anna Junior | Member - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Márcio Gomes Pinto Garcia | Member - non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Eduardo Cunha da Costa | Director - non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Ramiro Silveira Severo | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| João Verner Juenemann | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Rafael Andréas Weber | Member elected by minority common shareholders - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Adriano Cives Seabra | Member elected by minority preferred shareholders non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Márcio Kaiser | Member - appointed by the employees - non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
FISCAL COUNCIL
| Name | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bruno Pinto de Freitas | Sitting member, elected by majority shareholders- non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Rogério Costa Rokembach | Sitting member, elected by majority shareholders- non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Gustav Penna Gorski | Sitting member, elected by minority common shareholders - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Reginaldo Ferreira Alexandre | Sitting member, elected by preferred shareholders - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Bruno Queiroz Jatene | Alternate, elected by majority shareholders - non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Tanha Maria Lauermann Schneider | Alternate, elected by majority shareholders - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Vicente Jorge Soares Rodrigues | Alternate, elected by majority shareholders - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Paulo Roberto Franceschi | Alternate, elected by preferred shareholders - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
AUDIT COMMITTEE
| Name | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| João Verner Juenemann | Coordinator - non-executive position | Yes | 2020 - 2022 |
| Carlos Biedermann | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Eraldo Soares Peçanha | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
ELIGIBILITY AND COMPENSATION COMMITTEE
| Name | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arnaldo Bonoldi Dutra | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2024 |
| José Luiz Castro Mendel | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2024 |
| Giusepe Lo Russo | Member - non-executive position | No | 2021 - 2024 |
RISK COMMITTEE
| Name | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| João Zani | Coordinator - non-executive position | Yes | 2022 - 2024 |
| José Luis Campani Lourenzi | Member - non-executive position | No | 2022 - 2024 |
| Carlos Eduardo Schonerwald da Silva | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2022 - 2024 |
| Luanda Pereira Antunes | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
| Márcio Gomes Pinto Garcia | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2021 - 2023 |
SOCIAL, ENVIRONMENTAL AND CLIMATE RESPONSIBILITY COMMITTEE
| Member | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claíse Muller Rauber | Coordinator - Non-executive position | No | 2022 - 2023 |
| Wagner Lenhart | Member - non-executive position | No | 2022 - 2023 |
| Marivania Ghisleni Fontana | Member - non-executive position | No | 2022 - 2023 |
| Jorge Luís Tonetto | Member - non-executive position | No | 2022 - 2023 |
| Marilene de Oliveira Ramos Murias dos Santos | Member - non-executive position | Yes | 2023-2023¹ |
¹ Sworn in February 2023.
EXECUTIVE BOARD
| Name | Executive or non-executive position | Independent | Term of Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claudio Coutinho Mendes | CEO - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Irany de Oliveira Sant’Anna Junior | Deputy CEO and Risk and Controls Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Claíse Muller Rauber | Products, Segments and Digital Channels Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Fernando Postal | Distribution and Retail Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Jorge Fernando Krug Santos | IT and Innovation Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Marcus Vinícius Feijó Staffen | CFO and IRO - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Osvaldo Lobo Pires | Credit Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Wagner Lenhart | Institutional Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
| Marivania Ghisleni Fontana | Administrative Officer - executive position | No | 2021 - 2023 |
The Bank is exposed to transition risk arising from events associated with the transition to a low carbon economy, as well as legal and regulatory changes, technological innovations, changes in products and services supply and demand, unfavorable perception of clients, the financial market or society in general related to climate change.
Another risk that can impact the Institution is physical climate risk, which refers to the possibility of losses arising from frequent and severe weather conditions or long-term environmental changes. Examples of this type of risk include extreme weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, storms, cyclones, frosts and forest fires; and permanent environmental changes, including rising sea levels, scarcity of natural resources, desertification, and changes in rainfall or temperature patterns.
From the Integrated Risk Management process, in addition to monitoring the regulatory environment and customer perception, management includes consulting information on public lists and verifying the activities, products and services subject to social and environmental legislation. Therefore, the Institution seeks to ensure regularity at all levels of its operations. As for operations, Social, Environmental and Climate risks inherent to the activity’s economic industry are identified, based on the National Registry of Economic Activity (CNAE – Cadastro Nacional de Atividade Econômica) code.
Climate risk management costs are not calculated individually but are considered together with the resources allocated to the Institution’s risk management.
The joint development of commitments, indicators, and targets proposed by the Bank’s departments has been showing the topic’s greater maturity within the institution and the leadership’s stance. The main guideline is the Bank’s strategic planning, established by the ESG pillar.
The methodology used to create the agenda enabled a greater engagement of the units and executive offices, which had to work together and expand their knowledge. his is an ongoing process, but it is already possible to see advancements in the governance front. In order to prepare the ESG Agenda, Banrisul assessed internal and external information to obtain an overview of the efforts required to position itself aligned to market expectations. The Company used data from interviews with senior management and online stakeholder survey to prepare its materiality matrix, and meetings and workshops with key departments to get their opinion on suggested actions, targets and indicators.
The effectiveness of this measures is yet unknown, as their results will be seen after the due implementation of the 2030 Agenda.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resource / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESG Agenda is not prioritized by Senior Management | Negative | Actual | Short-term | One-time | Medium | Definition of the Company’s strategy. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Lack of ESG information to the market | Negative | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | High | Preparing external contents. | Shareholders and Investors, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Conflict of Interests, leading to controversial management | Negative | Potential | Short-term | Systemic | Medium | Senior management processes and activities. | Shareholders and Investors, Banrisul’s Operations. |
For policies and commitments related to this material topic, the Board of Directors approved the Social, Environmental and Climate Risk Policy (PRASC in Portuguese), which was published in June 2022 and aims to set out the guidelines for the Bank’s and Banrisul Group subsidiaries’ social, environmental and climate responsibility activities, aligned to the nature of their activities and the complexity of their products and services. The PRSAC seeks to foster sustainability, balancing business opportunities with social, economic, environmental and climate responsibilities, contributing to the sustainable development of the regions where Banrisul operates.
The Institutional Policy on Social, Environmental and Climate Risk Management, updated in 2022 based on new regulatory framework, is targeted at outlining the management processes, seeking to mitigate these risks and, consequently, safeguard the assets and interests of its customers, shareholders, employees and other stakeholders.
To manage the topic and its related impacts, Banrisul manages social, environmental and climate risks by identifying, measuring, assessing, monitoring, reporting, controlling and mitigating other corporate risks in an integrated way, keeping risk exposure at a level the Institution is willing to take and ensuring adherence to its Institutional Policies.
The Institution controls and mitigate potential negative impacts through initiatives and strategies that aim to keep exposure to social, environmental and climate risks at adequate levels. Risk treatment options are described and formalized through initiatives that can have one or more procedures and mitigate one or more risks.
Banrisul adopts a series of actions to mitigate potential negative impacts, mainly regarding the exposure of its credit operations, when applicable, i.e.:
– Contractual clauses determining that the borrower must comply with the respective legislation and adopt periodic monitoring;
– Contractual clauses foreseeing the possibility of early maturity of the operations in case of irregularities of this nature;
– Checking if environmental licenses and certificates are valid;
– Requiring the Biosafety Quality Certificate (CQB, in Portuguese), issued by the National Biosafety Technical Commission (CTNBio, in Portuguese);
– Applying the Survey of Indications of Contamination in Urban Properties (LIC, in Portuguese) form;
– Applying the social, environmental and climate risk analysis questionnaire, for operations above R$10 million;
– Monitoring agribusiness credit operations through the Social and Environmental Compliance System.
As regards its activities, Banrisul mitigates its exposure to potential negative impacts by adopting, among others, the listed action:
– In relevant contracting and procurement processes, it identifies the contracting risk matrix and social and environmental requirements.
The Institution identifies and remedies actual negative Social, Environmental and Climate (SAC, in Portuguese) impacts by consulting information in public lists and checking the activities, products and services subject to social and environmental legislation. As for operations, Social, Environmental and Climate Risks inherent to the activity’s economic industry are identified, based on the National Registry of Economic Activity (CNAE – Cadastro Nacional de Atividade Econômica) code.
As for the credit portfolio as a whole, Banrisul is developing a climate stress test model aimed at measuring the impact of climate events on the overall capital index, demonstrating the financial impact and defining new strategies for significant events.
The characteristics of the Institution’s products, services, activities and processes as well as the activities of its counter parties, controlled companies, suppliers and relevant outsourced service providers are assessed for potential risks of violation of fundamental rights and guarantees or acts harmful to the common interest; environmental degradation, including the excessive use of natural resources; and changes in weather patterns.
For each operational risk event, the Operational Losses Database identifies, when applicable, the operational losses linked to the Social, Environmental and Climate Risk. This scope is highlighted in civil and labor lawsuits, administrative proceedings, fines and other events.
To manage the positive impacts, the “Contribution to the Green Economy” indicator is monitored on a monthly basis to measure how much of the corporate credit portfolio is made up of economic sectors with a certain level of environmental and/or social contribution. This indicator is monitored by following up the percentage variation. The higher the percentage, the higher the active balance in financing to industries with a positive social and/or environmental impact, representing a higher contribution from the Institution.
The efficiency tracking processes are evaluated periodically, including assessing the internal and external audits, the Controls and Compliance department’s follow ups, operational risk analysis cycles, among other procedures. The Institution’s exposure to climate risk is monitored on a monthly basis, through the follow-up of the active balance of the corporate credit portfolio, allocated to industries with highly and moderate risk impacts.
The Bank also actively participates in FEBRABAN’s Committees and Working Groups, where it debates current relevant guidelines for this topic, participates in public consultations, and shares best practices with other companies in the industry.
As for goals, targets and indicators to assess progress based on Banrisul ESG Agenda’s recommendations, themes and strategic pillars were defined, and the Company set indicators and targets for strengthening management of social, environmental and climate risks and reducing climate risk.
Even though the Bank has robust risk management, there are still many opportunities to make progress in managing social, environmental and climate risks, especially in defining sensitive sectors and drafting restrictive policies. The recommendations of the ESG Agenda are based on Banrisul’s ongoing or planned actions/projects and the most prominent/most adopted actions by the financial industry.
In order to prepare the ESG Agenda, Banrisul assessed internal and external information to obtain an overview of the efforts required to position itself aligned to market expectations. The Company used data from interviews with senior management and online stakeholder survey to prepare its materiality matrix, and meetings and workshops with key departments to get their opinion on suggested actions, targets and indicators.
Moreover, Banrisul joined the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP in Portuguese) and the Brazilian GHG Protocol program to enhance its technical and institutional capacity in managing greenhouse gas emissions in order to take stock and report.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (Short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resource / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate change impacts on the Bank’s operation and the sale of its products and services (risk for the agribusiness segment - delinquency) | Negative | Actual | Medium-term | One-time | Medium | Credit assignment for agribusiness. The high concentration of the credit portfolio in customers whose economic industry is more likely to suffer financial impacts from climate change increases the Bank's exposure to physical climate risk. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Violation of fundamental rights and guarantees or acts harmful to the common interest | Negative | Potential | Long-term | Systemic | Medium | Financing to customers listed as employers of forced or compulsory labor | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Contribution to a green economy | Positive | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | - | Credit assignment based on an economic model that results in improved human welfare and social equality, while reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcity. | Shareholders andInvestors, Employees, Community, Customers, Suppliers, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Events related to the transition to a low-carbon economy | Negative | Potential | Long-term | Systemic | Medium | The high concentration of the credit portfolio in customers whose economic activity is connected to high GHG emissions increases the Bank's exposure to transition climate risk. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Suppliers, Environment, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Reduction of the exposure to loss ratio | Positive | Actual | Long-term | Systemic | - | Transition of the credit portfolio to less carbon-intensive industries | Shareholders andInvestors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Operational, financial and reputational impact from the response time to critical events (related to operational and credit risk) | Negative | Potential | Short-term | One-time | Medium | Comercial relationship with sensitive and carbon-intensive industries. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
The policies and commitments related to this material topic include financial education strategies focused on both the internal and external public, based on Bacen Notice 34,201/2019, the Organization’s Social, Environmental and Climate Responsibility Policy and the commitment made to Banrisul’s Strategic Sustainability Agenda.
To manage the topic and its impacts, the financial education strategy is implemented by the People Development Department — Corporate University connecting the working group with employees from several technical areas and from the branch network.
To prevent potential negative impacts of initiatives for young people and the community in general, the Bank designs a strategy jointly with the partner training institutions to follow up with young apprentices with the purpose to work on financial planning and organization; it also offers modules for young people participating in the Pescar (Fishing) Project and the Young Apprentice Program. In addition, webinars and content are developed on the Moodle platform, catering to the entire staff, including interns.
As for the actual negative impacts, in addition to the above-mentioned initiatives, based on the experience developed by branch managers, the working group and branch representatives co-create a training program for financial education multipliers acting in the communities, considering the appropriate content, activities and language for the different target audiences.
Regarding positive impacts, Banrisul also conducts a diagnosis of every strategy to be developed both for the internal and the external public, identifying their profile and potential vulnerabilities in order to adjust the content and language.
To track the effectiveness of the measures, surveys are conducted on the institutional social media focused on the external public. The staff also responds to surveys on the intranet, helping define topics for webinars and create content for the Moodle platform. For online or in-person lectures, workshops and courses, surveys are conducted immediately after the event, when it focuses on the internal public, and both before and after the event, when it caters to the external public.
The goals reached in 2022 include the launch of a financial education track for the staff on the Moodle platform, development of social media posts and the strategy of following up with young apprentices in the institutions that are part of the Program.
Monitoring of investments
| Year | R$ | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | No cost | - Drafting of an institutional primer;- Class developed for the 2020 Pescar Project by members of the Corporate University. |
| 2021 | R$2,524.00 | - Videos for the Global Money Week for young people from all over the country;- Webinars for Banrisul interns;- Class developed for the 2021 Pescar Project and the 2021 Apprentice Program by members of the working group. |
| 2022 | R$7,140.00 | - Webinars for Banrisul interns;- Production of a Financial Education course by the working group;- Class developed for the 2022 Pescar Project and the 2022 Apprentice Program by members of the working group. |
The financial education strategies and their respective indicators are now part of Banrisul’s Strategic Sustainability Agenda. The meetings to co-create strategies with the institutions that are part of the Young Apprentice Program helped identify alternatives to strengthen the bond and follow up with young people by offering financial education. In addition, demands from the community received by the branches drove the proposition of a program focused on capillarity through multipliers.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access of vulnerable groups and underserved markets to financial products and services | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | Acquisition of banking products, starting with financial planning and organization. | Community, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Conscious use of credit and better financial planning | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | Through Banrisul’s Financial Education Program, focused on the internal and external public, including young people from the Pescar Project and Young Apprentice Program | Employees, Community, Banrisul’s Operations. |
To govern supplier relations, Banrisul uses the Bidding Process Law (Federal Laws 8,666/93 and 13,303/2016), as well as other related federal and state laws. It also uses the Internal Regulations on Bidding Processes and Contracts (RILC, in Portuguese), which is published on the Institution’s transparency website. The transparency website also features other documents governing supplier relations, including the Supplier Relations Manual (which governs supplier behavior in bidding processes and the contracting of Banrisul Group companies) and Banrisul’s Supplier Manual (created to help Banrisul’s suppliers know and understand the procedures that the Company uses in its business relations for the acquisition of goods and services).
For the measures taken to manage the topic and its related impacts, there is not a specific position within the Organization to manage these impacts. They are mitigated throughout the supplier management chain, with different levels in charge of different tasks. For example, the Contract Management department is responsible for checking the documentation proving the bidder’s technical qualification in a bidding process; after the bidder becomes a contractor, the Contracting department is responsible for checking if the supplier has any impediments and if it has all the necessary certificates of good standing, among other things.
The measures to prevent or mitigate potential negative impacts include the existence of an Outsourcing Supervision department, which checks if the labor rights of outsourced workers that provide services for Banrisul are being respected. In order to mitigate impacts, Banrisul also created the Sanctioning Processes department, which is responsible for conducting administrative sanctioning processes that investigate negative incidents caused by the contractor and impose penalties, if applicable.
There are measures to face actual negative impacts, such as public contracting regulations, including a tool that mitigates the actual impact of the lack of supply of services or products by the contractor: emergency contracts. This legal provision enables the Bank to hire contractors to provide a portion of a service on an urgent basis, i.e., the services are provided first, and the internal administrative procedures set out in the regulations are completed later, formalizing the contract.
The Outsourcing Supervision department works to mitigate risks, but there is not yet a routine that provides information on how many defenses of complaints are successful. Regarding the Sanctioning Processes department, more penalties have been imposed over the periods, given that the managing departments understood the importance of effectively monitoring the performance of the contract and should request the determination of responsibility in case of irregularity in the provision of services by the contractor.
The effectiveness of the actions is felt qualitatively, as previously described, when the managing units are more concerned about describing possible penalties for the poor performance of the contract in the contracting processes; the managing units seek new ways to choose service providers through more robust qualifications in bidding processes; contractors try to anticipate future problems of understanding in requests of performance to the contractor, avoiding the filing of a sanctioning process; and contractors understand the importance of sending labor documentation to be effectively monitored by the Supervision department. The departments responsible for mitigating risks share what they have learned, guiding the continuous improvement of processes so that, given the right/duty of the managing department to start proceedings to determine responsibility in case of poor performance of the contract by the contractor, the contracting process is moralized, preventing possible market suppliers with bad intentions from participating in contracting procedures. Similarly, the effectiveness of Outsourcing Supervision can be reducing the number of labor complaints in which the Bank is jointly and severally liable.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reputational impact by association with irregular suppliers and commercial partners (labor and environmental issues) | Negative | Actual | Short-term | One-time | Low | Hiring of suppliers | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Reputation problems related to outsourced workers or commercial partners behaviors (such as discrimination and banking correspondents) | Negative | Actual | Short-term | One-time | High | Hiring of suppliers | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Operational problems related to outsourced workers strike | Negative | Potential | Short-term | One-time | Low | Services rendered by suppliers | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Community, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Leakage of confidential information by the supplier | Negative | Potential | Long-term | One-time | High | Services rendered by suppliers | Shareholders and Investors, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Operational problems due to suppliers not rendering services/delivering products | Negative | Actual | Short-term | One-time | Low | Services rendered by suppliers | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
The policies or commitments focused on human capital development are part of the “Strengthening People” front of Banrisul’s strategic planning, considering that employees are the means for achieving organizational success, thus the need for a fresher look and continuous encouragement to developing and improving people.
The People Development Superintendence Department – Corporate University is responsible for managing this topic and its impacts and reporting to the Executive Board. Its duties include “to manage the development, implementation and monitoring of in-person and distance education programs, seeking learning technologies solutions and contributing to the culture of innovation at Banrisul”. Furthermore, the HR areas share strategies and decision-making. The Annual Training Plan, which brings together all areas and Regional Superintendencies in its development, is analyzed jointly and submitted to the Committees and the Board of Directors for approval, accompanied by the respective budget plan.
The actions taken to address potential negative impacts include: onboarding of new employees; training programs for career development; academic incentive program, encompassing undergraduate, specialization, master’s and doctorate degrees; enrollment in paid external courses, refresher webinars on products, services, legislation and topics of interest, symposiums, congresses, among others; international missions; the reach of coursed offered via Moodle platform, favoring the ongoing development and incentive to self-development, regardless of geographical location.
Actions taken to address actual negative impacts include adapting educational technologies in order to provide a better experience for colleagues working at the branches by, for example, offering training sessions with audio and subtitles, enabling a better participation in the courses; organization of trails in different formats, promoting employees self-development. Offering more webinars on topics that attract a large audience, with the option of watching the recorded version for employees who, for different reasons, were not able to watch the presentation live.
Actions to manage actual and potential positive impacts: developing educational strategies and programs through co-production by integrating the branch network’s and general management’s point of view, focused on using knowledge to enhance productivity and provide better service; using inclusive and integrative language to inform about programs and development tracks; strengthening capacity building by bringing all units and Regional Superintendencies closer together through the employees’ academic research; making the final papers of graduating employees available so that research can be accessed by other employees and taken further.
In order to track the effectiveness of these actions, Banrisul monitors investments made, course attendance, certificates received, mandatory courses, career progression based on training programs; surveys the participants of courses and webinars; and verifies the applicability of academic research; among others.
The Annual Training and Development Plan’s strategy involves several stages, i.e., online survey available to all employees; focus groups with representatives from the Branch Network and General Management; analysis of strategic planning guidelines, market trends and gaps reported to the HR departments.
Banrisul evaluates corporate education based on the following indicators: investment, number of employees who attended courses, number of employees who received certification, training hours per employee, courses/events satisfaction level, courses/events quality level.
Periodically, quantitative data on trained employees are shared with the Executive Board and the entire staff in articles published in the internal portal. Moreover, every time Banrisul identifies a position that needs to be filed, specific training is developed to prepare professionals to meet the requirements of the job as market managers, business operators, agribusiness relationship managers, among others. Incentive to academic research encourages employees to share their work via banritalks and the virtual library, making knowledge accessible to the entire staff. Employees can request external and internal courses, such as webinars, via workflow, which enables the analysis, monitoring and conclusion of the process. Information on distance learning courses is published monthly, highlighting free and mandatory programs, in compliance with the legislation.
Given that finance is the Bank’s expertise and that employees should handle their own personal finances, a program was developed to offer financial education to all employees.
The branch network and General Management producing knowledge together enable sharing points of view that enhance the Annual Training Plan, as well as strategies for its implementation. Furthermore, the exchange with universities and innovation centers makes it possible to share challenges and solutions both for internal stakeholders and external groups and institutions.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of qualified human capital to the market | Negative | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | Low | Individual stage, where the employee does not perceive that his/her professional development is aligned to the periodicity and or benefits offered by the market, according to his/her qualification. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Human capital development | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | Incentive to Higher Education and access to the extensive portfolio of external and internal technical courses offered by Banrisul’s Distance Learning Platform and more assertive communication and more fluid processes. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Reduction in turnover | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | Initiatives to promote quality of life and benefits for internal stakeholders | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Banrisul’s Operations. | |
| Increase internal engagement | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | Internal communication initiatives, events/campaigns focused on internal stakeholders | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Increased investments in talent hiring, attraction, retention and training | Positive | Actual | Short-term | Systemic | Incentive to capacity building, training and succession plan considering management of competencies. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial impact on customers due to inadequate sales practices used by contractors/banking correspondents | Negative | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | Medium | Banking correspondents’ activities. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Impact from delinquency | Negative | Actual | Short-term | One-time | High | Customers’ indebtedness and compromised business sustainability | Shareholders and Investors, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations |
| Increase in vulnerability to data theft, coups and frauds | Negative | Actual | Short-term | One-time | Medium | Failures in sales activities. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Reputation in the use of personal data | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | One-time | - | Control of IT security systems and authorization to use personal data. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
Banrisul has an IT Security Unit, USTI in Portuguese, reporting to the Technology and Innovation Office. The USTI is responsible for Banrisul’s internal and external security culture and its structure supports Bank’s other Units in the design of new solutions and businesses. It is also responsible for proposing improvements to specific information security solutions.
The Unit participates in the Corporate Risk, Internal Controls & Compliance Management, and Information Technology Management Committees to evaluate whether information and cyber security issues were complied with in the propositions, new business solutions, internal control and risk assessments, and IT implementation and projects.
The USTI is also responsible for defining and maintaining the Information and Cyber Security Policy based on best practices and international standards, reinforcing the internal security and communication culture, establishing standards and rules to preserve the Bank’s assets and those of its customers. This policy should be reviewed at least every year.
To meet the ongoing and growing IT security demands, prevent and mitigate potential impacts and remediate actual impacts, the USTI:
- Prepares and manages the life cycle of security policies, such as the Information and Cyber Security Policy, the Business Continuity Plan and Internal IT Security Standards;
- Offers continuous training to employees who work in IT security and works closely with system suppliers;
- Runs security awareness campaigns targeted at customers and employees, especially the Safe Internet Day campaign and the Digital Security Week organized by FEBRABAN with the slogan “Stop & Think: it can be a scam!”;
- Monitors and fights fraud in Digital Channels, with constant update of the service channels security tools and resources;
- Uses cryptography and digital signatures, Security in Acquiring and Channels;
- Manages vulnerability, detects information security incidents at the Bank’s network and protects against malware by analyzing websites and applications made available by the Bank to its customers and employees and in its systems;
- Ensures Identity Management to control employee access to Banrisul IT resources and permissions;
- Participates in Bacen’s and FEBRABAN’s working groups;
- Supports the Bank’s departments that are directly involved in addressing the negative impacts generated by security incidents.
These campaigns are run every year and widely disseminated to customers on Banrisul’s social media and website, as well as to the Company’s staff on the Intranet. For the internal public, Banrisul released a new Distance Learning Program called Information Security, which includes the Security Manual for Working from Home. Banrisul has also been alerting its customers to IT security. The protective initiatives used by the Bank have prevented “Account Take-over” (ATO) attacks in which the hacker gains control of the customer’s checking account.
This continuous work allowed Banrisul to disseminate the culture of security, raising awareness and engaging all hierarchical levels, starting with senior management. Security processes and procedures to access service channels have been well accepted by customers. This shows that customers have embraced the security culture in their daily lives.
Positive impacts include participation in technology events that discuss security and the receipt of awards for solutions and products with outstanding security features.
The process used to verify the effectiveness of IT security actions are mostly related to compliance with the Information and Cyber Security Policy and feedback received through the business channels. The Policy is an important instrument to control and manage information security. It also lays down part of the actions taken by Banrisul to protect its IT assets.
Banrisul has not recorded relevant security incidents over the last few years. This shows the efficiency of the Bank’s anti-fraud procedures for its products such as Open Banking and API Market Place.
Setting Information Security goals, targets and indicators is a major challenge for Banrisul, as most of them are directly or indirectly susceptible to external factors or actions that depend on multiple parties.
| Impact | Classification (positive or negative) | Event (potential or actual) | Time frame (short-term or long-term) | Systemic or one-time impact | Irreversibility (high, medium, low - only for negative impacts) | Production chain process or activity that causes impact | Resources / stakeholder group impacted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of information security certificates | Negative | Potential | Long-term | One-time | Medium | Provision of human resources, materials and IT infrastructure to keep the certifications | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Community, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Optimization and process efficiency | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | In activities and processes that make services available with greater practicality and speed. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Services provided with better quality | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | Customer satisfaction and reduction in the number of complaints. | Shareholders and Investors, Employees, Customers, Community, Banrisul’s Operations. |
| Greater need for investments in new technologies and business process | Positive | Actual | Medium-term | Systemic | - | Quality of service provided. | Shareholders and Investors, Banrisul’s Operations. |
The Fiscal Council, through any of its members, is responsible for overseeing Management’s acts and verifying compliance with legal and statutory duties, according to the Fiscal Council’s Internal Regulation.
Banrisul does not have a policy on tax risk management. Some of the tax risks are identified, managed and monitored focused on Operational Risk, e.g., compliance with the legislation and rules.
The Operational Risk department identifies risks, whose control compliance are assessed by the Controls and Compliance department. Moreover, the Company has a whistleblowing channel, with a general scope that can receive reports on taxes.
Banrisul does not have a policy on tax risk management. Some of the tax risks are identified, managed and monitored focused on Operational Risk, e.g., compliance with the legislation and rules. The Fiscal Council, through any of its members, is responsible for overseeing and assessing Management’s acts and verifying compliance with legal and statutory duties, according to the Fiscal Council’s Internal Regulation. The Operational Risk department identifies risks, whose control compliance are assessed by the Controls and Compliance department.
Material Themes
Innovation & technology
The theme addresses the innovation of the Company’s processes, adoption of new technologies, research and development (R&D), and digital transformation of processes and products.
Sales practices and customer satisfaction
The topic addresses transparency in business practices and clear communication of product and service conditions, including training of bank correspondents on the topic and issues related to customer satisfaction and experience of the product/service provided.
Financial inclusion and education
The topic addresses the contribution to raising awareness among customers and non-customers about financial education and conscious use of money, and offering support and facilitated tools to expand access to financial products and services.
Sustainable products and businesses
The topic approaches the offering of services and products with positive economic, social and environmental impact. Some examples are: credit lines, solutions and products with a social and environmental focus, such as for small businesses, students, low-income population, access to housing, promotion of access to clean energy, reduction of water consumption, protection or support to biodiversity, etc.
Data privacy and security
The topic addresses the proper functioning of internal systems and security of customer information on the data network, ensuring compliance with General Law of Data Protection – LGPD.
Diversity & inclusion
The topic addresses issues such as employee and top management composition on diversity of gender, ethnicity, color, age, PwD, LGBTQIA+ identity, and other vulnerable groups.
Human capital development
The topic addresses the training and education of employees to develop and enhance work skills and knowledge.
Partners’ and suppliers’ management
The topic addresses task management and social and environmental regulatory compliance checks of contractors (suppliers and service providers). It includes preparation of third parties that deal with the public, such as security staff.
Eco-efficiency
The topic addresses the optimization of processes and activities, such as mechanisms to reduce the use of energy, water and/or waste, aiming at better financial performance and lower consumption of natural resources. It includes assessing and measuring the socio-environmental and economic impacts generated by products and services offered by the bank and operations, seeking greater eco-efficiency and maximization of positive impacts.
Environmental, social, and climate risk strategy
The topic addresses the Company’s strategy, governance, environmental, social and climate risk management for adaptation and resilience to the consequences of climate change for the business, such as storms, water shortages and new regulations. Includes management of greenhouse gases and other pollutant gases.
Corporate governance and integrity
The topic addresses the processes, culture, regulations, and strategy that define how a company is run. It includes Governance for Sustainability, which aims to advise the committees on the theme. It also involves the mechanisms applied by the company related to ethics, integrity, and anti-corruption, as well as the communication and accountability of internal actions to its stakeholders. It also includes compliance with market practices and sector regulations.
Risk approach and opportunities related to climate change
The approach used to foster opportunities related to climate change has a direct and indirect impact that can be positive, changing the society’s perception of institution’s management of climate-related and environmental matters, or negative with possible credit losses that can directly impact results expected by shareholders/investors, according to the control tools than can mitigate climate change-related events.
Social investment in the external community
Investing in the external community has a positive impact because it fosters the local economy through the sponsorships and leads to improvements to the quality of life of children, teenagers, and the elderly in situations of social vulnerability, through projects that develop skills and encourage sports, culture, and leisure. Consequently, this contributes to the access to banking services in the region.
Management of risks that can significantly impact business
Risk management has a direct and positive impact in the bank and its stakeholders for identifying and preventing possible security and privacy breaches to employees’ data and consequently customer data. A proper risk management ensures the institution’s soundness and the role it plays in society.
Criteria for financing assignment, positive impact and delinquency
The criteria adopted for the assignment of financing directly impact the Bank’s operations, as they impact investors’ decision-making, as well as new regulatory guidelines can impact criteria adopted. The strategic allocation of resources can foster the State’s social & economic development, as customers are directly impacted by the defined criteria. The Bank adopts criteria to minimize negative impacts, such as checking if the customer is listed as an “Employer of Forced Labor”, if they received environmental licenses or they have already caused environmental damage subject to conviction, and the absence of these criteria can generate negative impacts for the Bank.
Management of energy consumption and solid waste generation
How waste is managed has directly impacted the company, positively when waste generated is correctly disposed, showing the Bank’s concern with related social & environmental matters. However, it has negative environmental impacts when there are flaws in the proper final disposal of generated waste, which can reduce inclusion and income generation for recycling cooperatives. The use of incentivized and renewable energy generates a positive impact to stakeholders, which already demonstrates the Bank’s position towards environmental initiatives.
Business expansion strategy
Business expansion strategies have a positive impact due to the change in society’s behavior and the need to reduce environmental impacts, promoting more sustainable products combined with sustainable economic development.
Sustainable products and business
The offer of sustainable products that foster positive social and environmental impacts generates financial results and reputational gains. Suppliers and partners operations in line with the Bank’s institutional view can create positive impacts, however, by acting in disagreement with this view, they can have negative impacts. Society is positively impacted to the extent that products offered can contribute to improving quality of life and a sustainable income generation. Operating in the agribusiness sector can generate positive impacts by fostering sustainable practices, through financing lines and partnerships with services providers, however, it can pose negative impacts to the environment if credit is used to finance the use of pesticides or the purchase of diesel machines.
Innovation and Technology: digital operations, processes, products and services
Innovation and technology processes generate a series of positive impacts, e.g., increase the security of IT assets, as well as a better use of time by employees to serve customers, decreasing their operational load. Furthermore, this investment allows for financial citizenship, making the financial and payment system more accessible. Lastly, it fosters an increase in revenue as well as in customer satisfaction and loyalty and shows the company’s concern about the topic.
Quality of customer service and services provided
A good or bad service impacts the Bank. Nowadays, as there are service information rankings that can be easily visualized by the shareholders/ stakeholders, the company’s reputation and revenue are constantly linked to a good service and a good quality of the services provided.
